Page 851 - Krugmans Economics for AP Text Book_Neat
P. 851
S-5
SOLUTIONS TO AP REVIEW QUESTIONS
Price of Module 8
computer S 1
S 2
Check Your Understanding
P 1 E 1
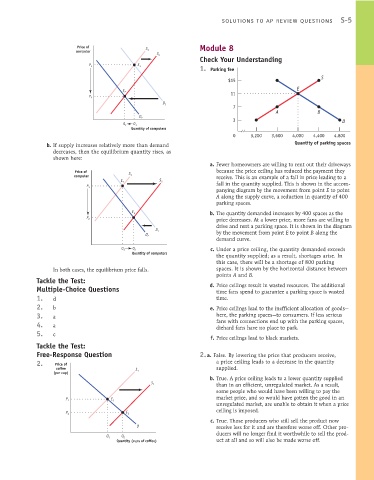
1. Parking fee
$15 S
E
E 2
11
P 2
D 1
7
A B
D 2
3 D
Q 2 Q 1
Quantity of computers
0 3,200 3,600 4,000 4,400 4,800
b. If supply increases relatively more than demand Quantity of parking spaces
decreases, then the equilibrium quantity rises, as
shown here:
a. Fewer homeowners are willing to rent out their driveways
Price of because the price ceiling has reduced the payment they
S 1
computer receive. This is an example of a fall in price leading to a
E 1 S 2
fall in the quantity supplied. This is shown in the accom-
P 1
panying diagram by the movement from point E to point
A along the supply curve, a reduction in quantity of 400
parking spaces.
b. The quantity demanded increases by 400 spaces as the
E 2
price decreases. At a lower price, more fans are willing to
P 2
drive and rent a parking space. It is shown in the diagram
D 1
by the movement from point E to point B along the
D 2
demand curve.
c. Under a price ceiling, the quantity demanded exceeds
Q 1 Q 2
Quantity of computers
the quantity supplied; as a result, shortages arise. In
this case, there will be a shortage of 800 parking
In both cases, the equilibrium price falls. spaces. It is shown by the horizontal distance between
points A and B.
Tackle the Test:
Multiple-Choice Questions d. Price ceilings result in wasted resources. The additional
time fans spend to guarantee a parking space is wasted
1. d time.
2. b e. Price ceilings lead to the inefficient allocation of goods—
3. a here, the parking spaces—to consumers. If less serious
4. a fans with connections end up with the parking spaces,
diehard fans have no place to park.
5. c
f. Price ceilings lead to black markets.
Tackle the Test:
Free-Response Question 2. a. False. By lowering the price that producers receive,
2. Price of a price ceiling leads to a decrease in the quantity
coffee supplied.
S 1
(per cup)
b. True. A price ceiling leads to a lower quantity supplied
than in an efficient, unregulated market. As a result,
S 2
some people who would have been willing to pay the
market price, and so would have gotten the good in an
P 1 E 1
unregulated market, are unable to obtain it when a price
ceiling is imposed.
P 2 E 2
c. True. Those producers who still sell the product now
D receive less for it and are therefore worse off. Other pro-
ducers will no longer find it worthwhile to sell the prod-
Q 1 Q 2
Quantity (cups of coffee) uct at all and so will also be made worse off.