Page 29 - Professorial Lecture - Prof Omoregie
P. 29
Zones of reduced oxygen can disrupt migratory patterns of pelagic fish
species and recruitment of species
Reduced biodiversity of benthic and pelagic communities, changes in the
trophic structure leading to lower fish production.
Increased levels of phosphate compounds are directly poisonous and
result in respiratory distress and tissue damage (Bwala and Omoregie,
2009)
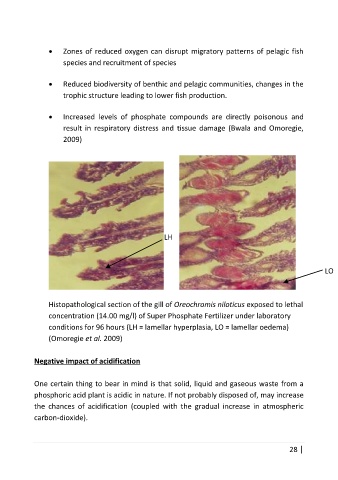
LH
LO
Histopathological section of the gill of Oreochromis niloticus exposed to lethal
concentration (14.00 mg/l) of Super Phosphate Fertilizer under laboratory
conditions for 96 hours (LH = lamellar hyperplasia, LO = lamellar oedema)
(Omoregie et al. 2009)
Negative impact of acidification
One certain thing to bear in mind is that solid, liquid and gaseous waste from a
phosphoric acid plant is acidic in nature. If not probably disposed of, may increase
the chances of acidification (coupled with the gradual increase in atmospheric
carbon-dioxide).
28 |