Page 121 - Demo
P. 121
d. is audit: Assessment of application level risks, IT infrastructure (Network, Operating systems, Database), IT processes / Operations and IT governance to assure information assets are protected and security risk is mitigated, are covered in this audit activity and / or Integrated audit activities wherein, the IT controls are reviewed, as part of an end-to-end coverage of business process along with General IS controls.
e. concurrent audit: As per RBI guidelines on Concurrent Audit System in Commercial Banks, Concurrent audit at branches should cover at least 50% of the advances and 50% of deposits of a bank. In addition to these, there are specific branches/ verticals which fall under the ambit of concurrent audit as per the RBI guidelines.
Accordingly the Bank identified the Branches that contributed to 50% of advances and 50% of deposits of the bank to be covered under concurrent audit. Similarly, few critical processes like Payments and Treasury function are also covered under concurrent audit. The Bank has put in place a Board approved separate Concurrent Audit Policy. On September 18, 2019, RBI has revised guidelines on Concurrent Audit and has advised to follow the Risk based approach in Concurrent Audit also. IAD has revised its policy & process and approved from ACB in January 2020. Accordingly w.e.f. April 1, 2020,theBranchidentificationandimplementationof Concurrent Audit activity is now in accordance with RBIA as prescribed by RBI.
In accordance with the IAD policy, all the auditors adhere to the code of ethics of Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) Inc. As professionals, members of IAD are additionally subject to the code of ethics of other professional bodies to which they belong like ICAI. IAD members apply and uphold the principles of Integrity, Objectivity, Competency and Confidentiality.
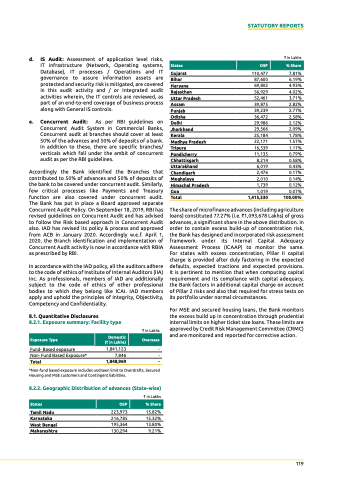
gujarat 110,477
` in Lakhs 7.81%
6.19%
4.93%
4.02%
3.71%
2.82%
2.77%
2.58%
2.12%
2.09%
1.78%
1.57%
1.17%
0.79%
0.58%
0.43%
0.17%
0.14%
0.12%
0.07%
100.00%
STATUTORY REPORTS
states
osP
% share
bihar
haryana
rajasthan
uttar Pradesh
assam
Punjab
odisha
delhi
Jharkhand
kerala
Madhya Pradesh
tripura
Pondicherry
chhattisgarh
uttarakhand
chandigarh
Meghalaya
himachal Pradesh
goa
87,600
69,802
56,929
52,461
39,875
39,239
36,472
29,986
29,566
25,184
22,171
16,539
11,135
8,214
6,019
2,476
2,010
1,739
1,019
total 1,415,330
8.1. Quantitative disclosures
8.2.1. exposure summary: Facility type
the share of microfinance advances (including agriculture loans) constituted 77.27% (i.e. `1,093,678 Lakhs) of gross advances, a significant share in the above distribution. In order to contain excess build-up of concentration risk, the Bank has designed and incorporated risk assessment framework under its Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) to monitor the same. For states with excess concentration, Pillar II capital charge is provided after duly factoring in the expected defaults, expected tractions and expected provisions. It is pertinent to mention that when computing capital requirement and its compliance with capital adequacy, the Bank factors in additional capital charge on account of Pillar 2 risks and also that required for stress tests on its portfolio under normal circumstances.
For MSE and secured housing loans, the Bank monitors the excess build up in concentration through prudential internal limits on higher ticket size loans. These limits are approved by Credit Risk Management Committee (CRMC) and are monitored and reported for corrective action.
exposure Type
domestic (` in Lakhs)
overseas
Fund- Based exposure
Non- Fund Based Exposure*
total
` in Lakhs
1,841,123 -
7,846 -
1,848,969 -
*Non-fund based exposure includes undrawn limit to Overdrafts, Secured Housing and MSE customers and Contingent liabilities.
8.2.2. geographic distribution of advances (state-wise)
states
osP
% share
tamil nadu
karnataka
West bengal
Maharashtra
223,973
216,785
195,364
130,294
` in Lakhs 15.82%
15.32%
13.80%
9.21%
119