Page 3 - Microeconomics
P. 3
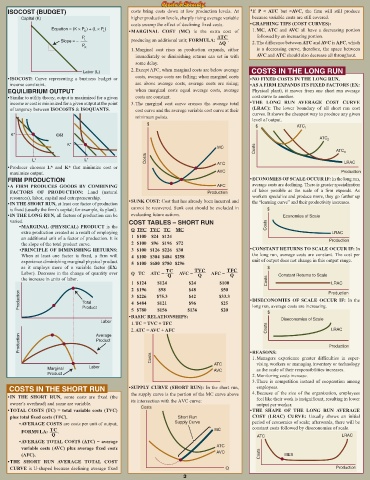
ISOCOST (BUDGET) costs bring costs down at low production levels. At *If P < ATC but >AVC, the firm will still produce
Capital (K) higher production levels, sharply rising average variable because variable costs are still covered.
costs swamp the effect of declining fixed costs. • GRAPHING TIPS (COST CURVES):
Equation = (K × P ) + (L × P ) 1. MC, ATC and AVC all have a decreasing portion
K L • MARGINAL COST (MC) is the extra cost of
P ∆TC followed by an increasing portion.
Slope = – L producing an additional unit; FORMULA: ∆Q . 2. The difference between ATC and AVC is AFC, which
P
K
1. Marginal cost rises as production expands, either is a decreasing curve; therefore, the space between
immediately or diminishing returns can set in with AVC and ATC should also decrease all throughout.
some delay.
Labor (L) 2. Except AFC, when marginal costs are below average COSTS IN THE LONG RUN
• ISOCOST: Curve representing a business budget or costs, average costs are falling; when marginal costs • NO FIXED COSTS IN THE LONG RUN.
income constraint. are above average costs, average costs are rising; • AS A FIRM EXPANDS ITS FIXED FACTORS (EX:
EQUILIBRIUM OUTPUT when marginal costs equal average costs, average Physical plant), it moves from one short run average
• Similar to utility theory, output is maximized for a given costs are constant. cost curve to another.
income or cost is minimized for a given output at the point 3. The marginal cost curve crosses the average total • THE LONG RUN AVERAGE COST CURVE
of tangency between ISOCOSTS & ISOQUANTS. cost curve and the average variable cost curve at their (LRAC): The lower boundary of all short run cost
minimum points. curves. It shows the cheapest way to produce any given
level of output.
$ $ ATC 1
K* OR
ATC 2
K*
MC Costs ATC 3
Costs
L* L* LRAC
• Producer chooses L* and K* that minimize cost or ATC
maximize output. AVC Production
FIRM PRODUCTION • ECONOMIES OF SCALE OCCUR IF: In the long run,
• A FIRM PRODUCES GOODS BY COMBINING AFC average costs are declining. There is greater specialization
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION: Land (natural Production of labor possible as the scale of a firm expands. As
resources), labor, capital and entrepreneurship. workers specialize and produce more, they go further up
• IN THE SHORT RUN, at least one factor of production • SUNK COST: Cost that has already been incurred and the “learning curve” and their productivity increases.
is fixed (usually the firm’s capital; for example, its plant). cannot be recovered. Sunk cost should be excluded in $
• IN THE LONG RUN, all factors of production can be evaluating future actions. Economies of Scale
varied. COST TABLES – SHORT RUN
• MARGINAL (PHYSICAL) PRODUCT is the Q TFC TVC TC MC Costs
extra production created as a result of employing LRAC
an additional unit of a factor of production. It is 1 $100 $24 $124 Production
the slope of the total product curve. 2 $100 $96 $196 $72
• PRINCIPLE OF DIMINISHING RETURNS: 3 $100 $126 $226 $30 • CONSTANT RETURNS TO SCALE OCCUR IF: In
When at least one factor is fixed, a firm will 4 $100 $384 $484 $258 the long run, average costs are constant. The cost per
experience diminishing marginal physical product 5 $100 $680 $780 $296 unit of output does not change in this output range.
as it employs more of a variable factor (EX: $
Labor). Decrease in the change of quantity over Q TC ATC = TC AVC = TVC AFC = TFC Constant Returns to Scale
Q
Q
Q
the increase in units of labor.
1 $124 $124 $24 $100 Costs LRAC
2 $196 $98 $48 $50 Production
Production Total 3 $226 $75.3 $42 $33.3 • DISECONOMIES OF SCALE OCCUR IF: In the
4 $484
$25
$96
$121
long run, average costs are increasing.
Product
5 $780
$156
• BASIC RELATIONSHIPS: $136 $20 $
Labor 1. TC = TVC + TFC Diseconomies of Scale
2. ATC = AVC + AFC Costs LRAC
Average
Production Product Production
Costs • REASONS:
1. Managers experience greater difficulties in super-
Marginal Labor ATC vising workers or managing inventory or technology
as the scale of their responsibilities increases.
AVC
Product 2. Monitoring costs increase.
3. There is competition instead of cooperation among
COSTS IN THE SHORT RUN • SUPPLY CURVE (SHORT RUN): In the short run, employees.
• IN THE SHORT RUN, some costs are fixed (the the supply curve is the portion of the MC curve above 4. Because of the size of the organization, employees
feel like their work is insignificant, resulting in lower
owner’s overhead) and some are variable. its intersection with the AVC curve: output per worker.
• TOTAL COSTS (TC) = total variable costs (TVC) Costs • THE SHAPE OF THE LONG RUN AVERAGE
plus total fixed costs (TFC). Short Run COST (LRAC) CURVE: Usually shows an initial
• AVERAGE COSTS are costs per unit of output; Supply Curve period of economies of scale; afterwards, there will be
FORMULA: TC . MC constant costs followed by diseconomies of scale.
Q ATC LRAC
• AVERAGE TOTAL COSTS (ATC) = average
variable costs (AVC) plus average fixed costs ATC
(AFC). AVC Costs MES
• THE SHORT RUN AVERAGE TOTAL COST
CURVE is U-shaped because declining average fixed Q Production
3