Page 2 - Science Fundamentals 2
P. 2
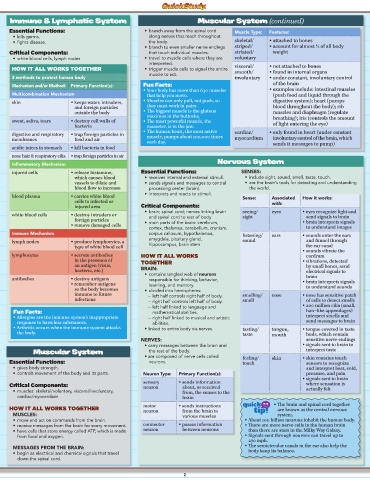
Immune & Lymphatic System Muscular System (continued)
Essential Functions: • branch away from the spinal cord Muscle Type: Features:
• kills germs. along nerves that reach throughout
• fights disease. the body. skeletal/ • attached to bones
• branch to even smaller nerve endings striped/ • account for almost ½ of all body
Critical Components: that touch individual muscles. striated/ weight
• white blood cells, lymph nodes • travel to muscle cells where they are voluntary
interpreted.
How It All worKs togEtHEr • trigger muscle cells to signal the entire visceral/ • not attached to bones
muscle to act. smooth/ • found in internal organs
3 methods to protect human body involuntary • under constant, involuntary control
Mechanism and/or Method: Primary Function(s): Fun Facts: of the brain
• Your body has more than 630 muscles • examples include: intestinal muscles
Multicombination Mechanism that help you move. (push food and liquid through the
skin • keeps water, intruders, • Muscles can only pull, not push, so digestive system); heart (pumps
and foreign particles they must work in pairs. blood throughout the body); rib
outside the body • The biggest muscle is the gluteus muscles and diaphragm (regulate
maximus in the buttocks. breathing); iris (controls the amount
sweat, saliva, tears • destroy cell walls of • The most powerful muscle, the of light entering the eye)
bacteria masseter, is in the jaw.
• The human heart, the most active cardiac/ • only found in heart (under constant
digestive and respiratory • trap foreign particles in muscle, pumps about 100,000 times
membranes food and air each day. myocardium involuntary control of the brain, which
sends it messages to pump)
acidic juices in stomach • kill bacteria in food
nose hair & respiratory cilia • trap foreign particles in air
Inflammatory Mechanism Nervous System
injured cells • release histamine, Essential Functions: SENSES:
which causes blood • receives internal and external stimuli. • include sight, sound, smell, taste, touch.
vessels to dilate and • sends signals and messages to central • are the brain’s tools for detecting and understanding
blood flow to increase processing center (brain). the world.
• interprets and reacts to stimuli.
blood plasma • carries white blood Sense: Associated How it works:
cells to infected or with:
injured area Critical Components:
• brain; spinal cord; nerves linking brain seeing/ eyes • eyes recognize light and
white blood cells • destroy intruders or and spinal cord to rest of body sight send signals to brain
foreign particles • brain interprets signals
• remove damaged cells • main parts of the brain: cerebrum,
cortex, thalamus, cerebellum, cranium, to understand images
Immune Mechanism corpus callosum, hypothalamus, listening/ ears • sounds enter the ears
amygdala, pituitary gland,
lymph nodes • produce lymphocytes, a sound and funnel through
type of white blood cell hippocampus, brain stem the ear canal
• sounds vibrate the
lymphocytes • secrete antibodies How It All worKs eardrum
in the presence of togEtHEr • vibrations, detected
an antigen (virus, by small bones, send
bacteria, etc.) bRAIN: electrical signals to
• contains tangled web of neurons
antibodies • destroy antigens responsible for thinking, behavior, brain
• remember antigens learning, and memory. • brain interprets signals
so the body becomes • divided into hemispheres: to understand sounds
immune to future – left half controls right half of body. smelling/ nose • nose has sensitive patch
infections – right half controls left half of body. smell of cells to detect smells
– left half linked to language and • 200 million cilia (small,
Fun Facts: mathematical abilities. hair-like appendages)
• Allergies are the immune system’s inappropriate – right half linked to musical and artistic interpret smells and
response to harmless substances. abilities. send messages to brain
• Arthritis occurs when the immune system attacks • linked to entire body via nerves. tasting/ tongue, • tongue covered in taste
the body. taste mouth buds, which contain
NERvES: sensitive nerve endings
• carry messages between the brain and • signals sent to brain to
Muscular System the rest of the body. interpret taste
• are composed of nerve cells called feeling/ skin • skin contains touch
Essential Functions: neurons. touch sensors to recognize
• gives body strength. and interpret heat, cold,
• controls movement of the body and its parts. Neuron Type: Primary Function(s): pressure, and pain
• signals sent to brain
sensory • sends information
Critical Components: neuron about, or received Quick J where sensation is
• muscles: skeletal/voluntary, visceral/involuntary, from, the senses to the Tip! actually felt
cardiac/myocardium brain
motor • sends instructions Quick J • The brain and spinal cord together
How It All worKs togEtHEr neuron from the brain to Tip! are known as the central nervous
MuScLES: various muscles system.
• move and act on commands from the brain. • About 100 billion neurons inhabit the human body.
• There are more nerve cells in the human brain
• receive messages from the brain for every movement. connector • passes information Quick J
Tip!
• have cells that store energy called ATP, which is made neuron between neurons than there are stars in the Milky Way Galaxy.
from food and oxygen. • Signals sent through neurons can travel up to
270 mph.
Quick J
MESSAGES FRoM THE bRAIN: • The semicircular canals in the ear also help the
Tip!
• begin as electrical and chemical signals that travel body keep its balance.
down the spinal cord.
2