Page 3 - Science Fundamentals 2
P. 3
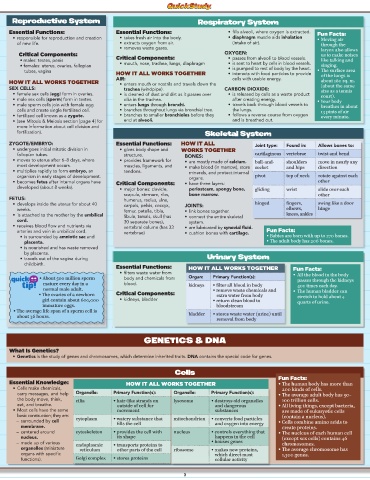
Reproductive System Respiratory System
Muscle Type: Features: Essential Functions: Essential Functions: • fills alveoli, where oxygen is extracted. Fun Facts:
• responsible for reproduction and creation • takes fresh air into the body. • diaphragm muscle aids inhalation
skeletal/ • attached to bones • extracts oxygen from air. (intake of air). • Moving air
striped/ • account for almost ½ of all body of new life. • removes waste gases. through the
striated/ weight Critical Components: oxyGEN: larynx also allows
voluntary Critical Components: • passes from alveoli to blood vessels. us to make noises
• males: testes, penis like talking and
visceral/ • not attached to bones • females: uterus, ovaries, fallopian • mouth, nose, trachea, lungs, diaphragm • is sent to heart by cells in blood vessels. singing.
• is pumped to rest of body by the heart.
smooth/ • found in internal organs tubes, vagina How It All worKs togEtHEr • interacts with food particles to provide • The surface area
involuntary • under constant, involuntary control AIR: cells with usable energy. of the lungs is
about 160 sq. m.
of the brain How It All worKs togEtHEr • enters mouth or nostrils and travels down the (about the same
• examples include: intestinal muscles SEx cELLS: trachea (windpipe). cARboN DIoxIDE: size as a tennis
(push food and liquid through the • female sex cells (egg) form in ovaries. • is cleaned of dust and dirt as it passes over • is released by cells as a waste product court).
digestive system); heart (pumps • male sex cells (sperm) form in testes. cilia in the trachea. after creating energy. • Your body
blood throughout the body); rib • male sperm cells join with female egg • enters lungs through bronchi. • travels back through blood vessels to breathes in about
the lungs.
muscles and diaphragm (regulate cells and create single fertilized cell. • branches throughout lungs via bronchial tree. • follows a reverse course from oxygen 13 pints of air
• branches to smaller bronchioles before they
breathing); iris (controls the amount • fertilized cell known as a zygote. end at alveoli. and is breathed out. every minute.
of light entering the eye) • (see Mitosis & Meiosis section [page 4] for
more information about cell division and
cardiac/ • only found in heart (under constant fertilization). Skeletal System
myocardium involuntary control of the brain, which
sends it messages to pump) zyGoTE/EMbRyo: Essential Functions: How It All joint type: Found in: Allows bones to:
• undergoes initial mitotic division in • gives body shape and worKs togEtHEr
fallopian tubes. structure. boNES: cartilaginous vertebrae twist and bend
• moves to uterus after 6–8 days, where • provides framework for • are mostly made of calcium. ball-and- shoulders move in nearly any
most development occurs. muscles, ligaments, and • make blood (in marrow), store socket and hips direction
• multiplies rapidly to form embryo, an tendons. minerals, and protect internal
organism in early stages of development. organs. pivot top of neck rotate against each
• becomes fetus after internal organs have Critical Components: • have three layers: other
developed (about 8 weeks). • major bones: clavicle, periosteum, spongy bone, gliding wrist slide over each
scapula, sternum, ribs, bone marrow. other
Sense: Associated How it works: FETuS: humerus, radius, ulna,
with: • develops inside the uterus for about 40 carpals, pelvis, coccyx, joINTS: hinged fingers, swing like a door
seeing/ eyes • eyes recognize light and weeks. femur, patella, tibia, • link bones together. elbows, hinge
knees, ankles
sight send signals to brain • is attached to the mother by the umbilical fibula, tarsals, skull (has • connect the entire skeletal
• brain interprets signals cord. 30 separate bones), system.
to understand images • receives blood flow and nutrients via vertebral column (has 33 • are lubricated by synovial fluid.
arteries and vein in umbilical cord. vertebrae) • cushion bones with cartilage. Fun Facts:
listening/ ears • sounds enter the ears • is surrounded by amniotic sac and • Babies are born with up to 270 bones.
sound and funnel through placenta. • The adult body has 206 bones.
the ear canal • is nourished and has waste removed
• sounds vibrate the by placenta.
eardrum Quick J urinary System
• vibrations, detected • travels out of the vagina during
Tip!
by small bones, send childbirth. Essential Functions: How It All worKs togEtHEr Fun Facts:
electrical signals to • filters waste water from
brain J • About 500 million sperm body and chemicals from organ: Primary Function(s): • All the blood in the body
• brain interprets signals Quick mature every day in a blood. passes through the kidneys
to understand sounds Tip! normal male adult. kidneys • filter all blood in body 400 times each day.
• remove waste chemicals and
smelling/ nose • nose has sensitive patch • The ovaries of a newborn Critical Components: extra water from body • The human bladder can
stretch to hold about 4
smell of cells to detect smells Quick J girl contain about 600,000 • kidneys, bladder • return clean blood to quarts of urine.
• 200 million cilia (small, Tip! immature eggs. bloodstream
hair-like appendages) • The average life span of a sperm cell is
interpret smells and about 36 hours. bladder • stores waste water (urine) until
send messages to brain Quick J removal from body
tasting/ tongue, • tongue covered in taste Tip!
taste mouth buds, which contain
sensitive nerve endings GeNeTICS & DNA
• signals sent to brain to
interpret taste what Is genetics?
feeling/ skin • skin contains touch • Genetics is the study of genes and chromosomes, which determine inherited traits. DNA contains the special code for genes.
touch sensors to recognize
and interpret heat, cold,
pressure, and pain Cells
• signals sent to brain Fun Facts:
where sensation is Essential Knowledge: How It All worKs togEtHEr • The human body has more than
actually felt • Cells make chemicals, 200 kinds of cells.
carry messages, and help organelle: Primary Function(s): organelle: Primary Function(s): • The average adult body has 50–
the body move, think, cilia • hair-like strands on lysosome • destroys old organelles 100 trillion cells.
eat, and breathe. outside of cell for and dangerous • All living things, except bacteria,
• Most cells have the same movement substances are made of eukaryotic cells
basic construction; they are: (contain a nucleus).
– surrounded by cell cytoplasm • watery substance that mitochondrion • converts food particles • Cells combine amino acids to
and oxygen into energy
fills the cell
membrane. create proteins.
– centered around cytoskeleton • provides the cell with nucleus • controls everything that • The nucleus of each human cell
nucleus. its shape happens in the cell (except sex cells) contains 46
– made up of various endoplasmic • transports proteins to • houses genes chromosomes.
organelles (miniature reticulum other parts of the cell ribosome • makes new proteins, • The average chromosome has
organs with specific which direct most 1,300 genes.
functions). Golgi complex • stores proteins cellular activity
3