Page 61 - ESP (CNG & LNG) Participant Guide
P. 61
Module 8: LNG Vehicle Systems and Safety Practices
Lesson 8.1: Two Types of LNG Fuel Systems
Saturated LNG Make up approximately 90% of all LNG systems operating today
Systems “Saturated” refers to the amount of heat that has been absorbed by the fuel
Also known as “conditioned”
LNG is warmed to approximately -200 F, 100 psi
o
Supply fuel for Cummins natural gas engines
Unsaturated LNG Make up approximately 10% of LNG systems operating today
Systems Also known as “unconditioned”
o
Fuel is cold approximately -230 F, approximately 30 psi
Supply fuel for Westport 15 L HPDI engines (discontinued)
Lesson 8.2: Saturated LNG Fuel Systems and Components
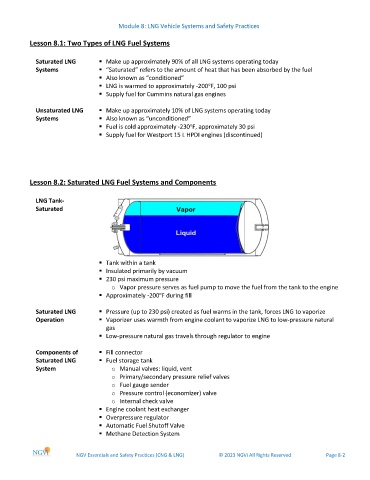
LNG Tank-
Saturated
Tank within a tank
Insulated primarily by vacuum
230 psi maximum pressure
o Vapor pressure serves as fuel pump to move the fuel from the tank to the engine
o
Approximately -200 F during fill
Saturated LNG Pressure (up to 230 psi) created as fuel warms in the tank, forces LNG to vaporize
Operation Vaporizer uses warmth from engine coolant to vaporize LNG to low-pressure natural
gas
Low-pressure natural gas travels through regulator to engine
Components of Fill connector
Saturated LNG Fuel storage tank
System o Manual valves: liquid, vent
o Primary/secondary pressure relief valves
o Fuel gauge sender
o Pressure control (economizer) valve
o Internal check valve
Engine coolant heat exchanger
Overpressure regulator
Automatic Fuel Shutoff Valve
Methane Detection System
NGV Essentials and Safety Practices (CNG & LNG) © 2023 NGVi All Rights Reserved Page 8-2