Page 63 - ESP Participant Guide_Neat
P. 63
Module 8: LNG Vehicle Systems and Safety Practices
Lesson 8.1: Two Types of LNG Fuel Systems
Saturated LNG ▪ Make up approximately 90% of all LNG systems operating today
Systems ▪ “Saturated” refers to the amount of heat that has been absorbed by the fuel
▪ Also known as “conditioned”
o
▪ LNG is warmed to approximately -200 F, 100 psi
▪ Supply fuel for Cummins natural gas engines
Unsaturated LNG ▪ Make up approximately 10% of LNG systems operating today
Systems ▪ Also known as “unconditioned”
o
▪ Fuel is cold approximately -230 F, approximately 30 psi
▪ Supply fuel for Westport 15 L HPDI engines (discontinued)
Lesson 8.2: Saturated LNG Fuel Systems and Components
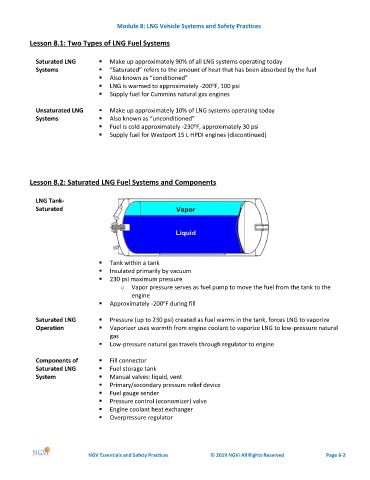
LNG Tank-
Saturated
▪ Tank within a tank
▪ Insulated primarily by vacuum
▪ 230 psi maximum pressure
o Vapor pressure serves as fuel pump to move the fuel from the tank to the
engine
o
▪ Approximately -200 F during fill
Saturated LNG ▪ Pressure (up to 230 psi) created as fuel warms in the tank, forces LNG to vaporize
Operation ▪ Vaporizer uses warmth from engine coolant to vaporize LNG to low-pressure natural
gas
▪ Low-pressure natural gas travels through regulator to engine
Components of ▪ Fill connector
Saturated LNG ▪ Fuel storage tank
System ▪ Manual valves: liquid, vent
▪ Primary/secondary pressure relief device
▪ Fuel gauge sender
▪ Pressure control (economizer) valve
▪ Engine coolant heat exchanger
▪ Overpressure regulator
NGV Essentials and Safety Practices © 2019 NGVi All Rights Reserved Page 8-2