Page 142 - Merton SuDS Design and Evaluation Guide
P. 142
Detailed Design 9.11.5 Storage structures The introduction of geocellular structures is In addition, to the statements from the SuDS Where underground storage is preferred Detailed Design
Manual the following should also be
after a full exploration of the available
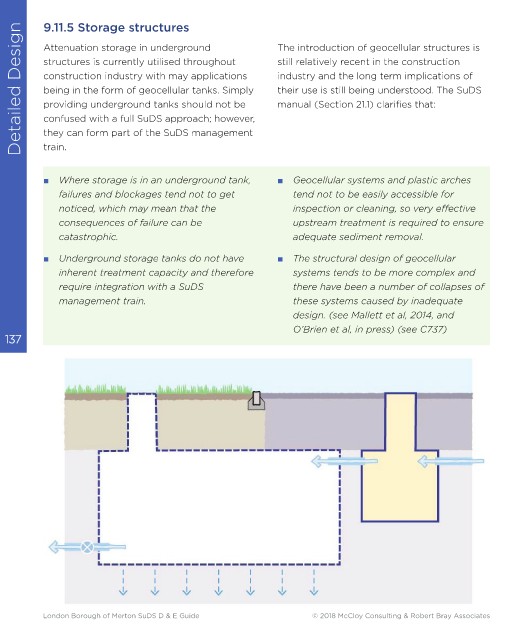
Attenuation storage in underground
considered:
options the designer should demonstrate
still relatively recent in the construction
structures is currently utilised throughout
that:
■
There are risks of structural failure due to
construction industry with may applications
industry and the long term implications of
construction loading, which may exceed
■
Robust silt removal has been provided
being in the form of geocellular tanks. Simply
their use is still being understood. The SuDS
design life loading that the designer may
through means of filtration (bioretention,
providing underground tanks should not be
manual (Section 21.1) clarifies that:
not be aware of.
permeable pavement) or other source
confused with a full SuDS approach; however,
they can form part of the SuDS management
■
There are a wide range of attenuation
not be accepted as a demonstrable form
train.
products each with its own loading
of silt removal. The SuDS manual (Section
characteristics. Surety must be provided control SuDS components. Catchpits will
■ Where storage is in an underground tank, ■ Geocellular systems and plastic arches that a specified product is not swapped 4.1) clarifies that sediments within
failures and blockages tend not to get tend not to be easily accessible for for one of inferior quality during the catchpits can be remobilised and washed
noticed, which may mean that the inspection or cleaning, so very effective construction phase. downsteam. Equally, gullypots are
consequences of failure can be upstream treatment is required to ensure ■ suggested by Table 26.15 to provide
catastrophic. adequate sediment removal. Guarantees and warranties are dependent negligible to zero treatment (Ellis et al,
on the survival of product manufacturers. 2012).
■ Underground storage tanks do not have ■ The structural design of geocellular
inherent treatment capacity and therefore systems tends to be more complex and ■ Underground structures require structural
require integration with a SuDS there have been a number of collapses of design consideration even if they are not
receiving vehicular loading. CIRIA report
management train. these systems caused by inadequate
design. (see Mallett et al, 2014, and C737 outlines the design requirements for
geocellular tanks. The SuDS Manual
O’Brien et al, in press) (see C737)
137 (Table 21.1) provides a summary of the 138
structural design requirements using a risk
classification system (Scored between
0-3). Designers should demonstrate that
the classification system has been
followed and present the appropriate level
of design information accordingly.
Design Note:
Where the stated design life of the tank does not meet the design life of the development,
the design should demonstrate how the structure will be replaced whist maintaining the
functionality of the drainage system and the scheme. Consideration should also be given to
funding mechanism for undertaking these replacement works.
London Borough of Merton SuDS D & E Guide © 2018 McCloy Consulting & Robert Bray Associates London Borough of Merton SuDS D & E Guide © 2018 McCloy Consulting & Robert Bray Associates