Page 147 - Merton SuDS Design and Evaluation Guide
P. 147
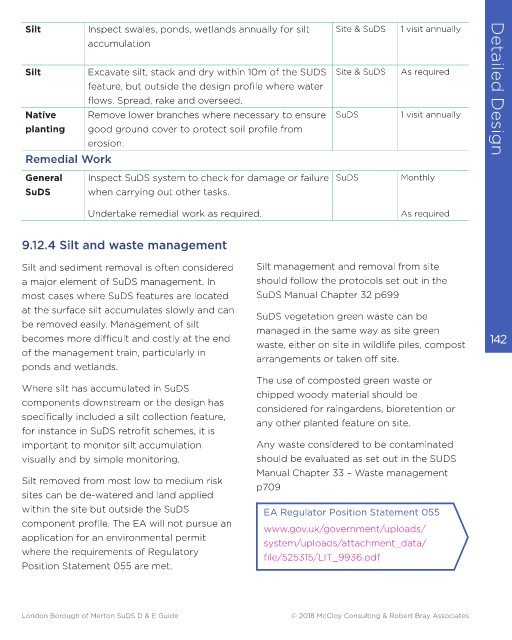
Detailed Design 9.12.3 Example of SuDS and Site Maintenance Normal site Suggested Silt Inspect swales, ponds, wetlands annually for silt Site & SuDS 1 visit annually Detailed Design
accumulation
Silt
Excavate silt, stack and dry within 10m of the SUDS Site & SuDS
As required
care (Site) or
feature, but outside the design profile where water
Activity
Type
SuDS-specific
frequency
flows. Spread, rake and overseed.
maintenance
Native
1 visit annually
Remove lower branches where necessary to ensure SuDS
(SuDS)
Regular Maintenance
erosion.
Pick up all litter in SUDS Landscape areas along
LItter
Remedial Work
with remainder of the site – remove from site Site 1 visit monthly planting good ground cover to protect soil profile from
Grass Mow all grass verges, paths and amenity grass at Site As required or General Inspect SuDS system to check for damage or failure SuDS Monthly
35-50mm with 75mm max. Leaving cuttings in situ 1 visit monthly SuDS when carrying out other tasks.
Grass Mow all dry swales, dry SUDS basins and margins Site 4-8 visits per Undertake remedial work as required. As required
to low flow channels and other SUDS features at year or as
100mm with 150mm max. Cut wet swales or basins required 9.12.4 Silt and waste management
annually as wildflower areas – 1st and last cuts to be
collected Silt and sediment removal is often considered Silt management and removal from site
Grass Wildflower areas strimmed to 100mm in Sept or at Site 1 visit annually a major element of SuDS management. In should follow the protocols set out in the
end of school holidays – all cuttings removed most cases where SuDS features are located SuDS Manual Chapter 32 p699
Or at the surface silt accumulates slowly and can
SuDS vegetation green waste can be
Wildflower areas strimmed to 100mm on 3 year be removed easily. Management of silt managed in the same way as site green
141 rotation – 30% each year – all cuttings removed 1 visit annually becomes more difficult and costly at the end waste, either on site in wildlife piles, compost 142
inlets & Inspect monthly, remove silt from slab aprons and SuDS 1 visit monthly of the management train, particularly in arrangements or taken off site.
outlets debris. Strim 1m round for access ponds and wetlands.
The use of composted green waste or
Permeable Sweep all paving regularly to keep surface tidy Site 1 visit annually Where silt has accumulated in SuDS
paving or as required components downstream or the design has chipped woody material should be
considered for raingardens, bioretention or
specifically included a silt collection feature,
Occasional Tasks any other planted feature on site.
for instance in SuDS retrofit schemes, it is
Permeable Sweep and suction brush permeable paving when SuDS As required - important to monitor silt accumulation Any waste considered to be contaminated
paving ponding occurs estimate 10-15 visually and by simple monitoring. should be evaluated as set out in the SUDS
year intervals Manual Chapter 33 – Waste management
Flow Annual inspection of control chambers - remove silt SuDS 1 visit annually Silt removed from most low to medium risk p709
controls and check free flow sites can be de-watered and land applied
within the site but outside the SuDS EA Regulator Position Statement 055
Wetland & Wetland vegetation to be cut at 100mm on 3 – 5 Site As required component profile. The EA will not pursue an
pond year rotation or 30% each year. All cuttings to be application for an environmental permit www.gov.uk/government/uploads/
removed to wildlife piles or from site. system/uploads/attachment_data/
where the requirements of Regulatory
file/525315/LIT_9936.pdf
Position Statement 055 are met.
London Borough of Merton SuDS D & E Guide © 2018 McCloy Consulting & Robert Bray Associates London Borough of Merton SuDS D & E Guide © 2018 McCloy Consulting & Robert Bray Associates