Page 31 - JulAug2019_BarJournal
P. 31
FAMILY LAW FEATURE
Health Insurance (R.C. 3119.30) Child Care (R.C. 3119.05) • Significant in-kind contributions from a
The custodial parent is now rebuttably There are now caps on allowable child care parent, including, but not limited to, direct
presumed to be the health insurance obligor. expenses added to the basic obligation because payment for lessons, sports equipment,
Health insurance is costly, and the total out-of- high child care built into the calculation made schooling, or clothing
pocket cost of health insurance must now be support unaffordable to low income obligors. • Extraordinary work-related expenses incurred
used in deciding whether the cost of coverage is
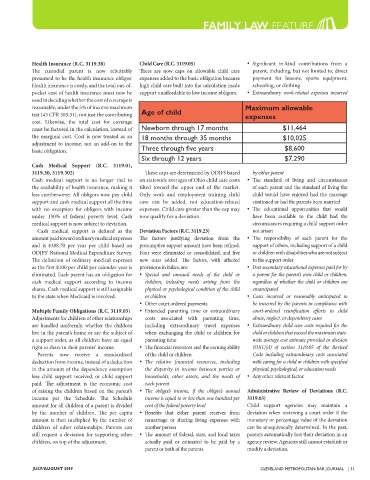
reasonable, under the 5% of income maximum Maximum allowable
test (45 CFR 303.31), not just the contributing Age of child expenses
cost. Likewise, the total cost for coverage
must be factored in the calculation, instead of Newborn through 17 months $11,464
the marginal cost. Cost is now treated as an 18 months through 35 months $10,025
adjustment to income, not an add-on to the
basic obligation. Three through five years $8,600
Six through 12 years $7,290
Cash Medical Support (R.C. 3119.01,
3119.30, 3119.302) These caps are determined by ODJFS based by either parent
Cash medical support is no longer tied to on statewide averages of Ohio child care costs • The standard of living and circumstances
the availability of health insurance, making it tilted toward the upper end of the market. of each parent and the standard of living the
less cumbersome. All obligors now pay child Only work and employment training child child would have enjoyed had the marriage
support and cash medical support all the time care can be added, not education-related continued or had the parents been married
with no exception for obligors with income expenses. Child care greater than the cap may • The educational opportunities that would
under 150% of federal poverty level. Cash now qualify for a deviation. have been available to the child had the
medical support is now subject to deviation. circumstances requiring a child support order
Cash medical support is defined as the Deviation Factors (R.C. 3119.23) not arisen
amount paid toward ordinary medical expenses The factors justifying deviation from the • The responsibility of each parent for the
and is $388.70 per year per child based on presumptive support amount have been refined. support of others, including support of a child
ODJFS’ National Medical Expenditure Survey. Four were eliminated or consolidated, and five or children with disabilities who are not subject
The definition of ordinary medical expenses new ones added. The factors, with affected to the support order
as the first $100 per child per calendar year is provisions in italics, are: • Post-secondary educational expenses paid for by
eliminated. Each parent has an obligation for • Special and unusual needs of the child or a parent for the parent’s own child or children,
cash medical support according to income children, including needs arising from the regardless of whether the child or children are
shares. Cash medical support is still assignable physical or psychological condition of the child emancipated
to the state when Medicaid is involved. or children • Costs incurred or reasonably anticipated to
• Other court ordered payments be incurred by the parents in compliance with
Multiple Family Obligations (R.C. 3119.05) • Extended parenting time or extraordinary court-ordered reunification efforts in child
Adjustments for children of other relationships costs associated with parenting time, abuse, neglect, or dependency cases
are handled uniformly, whether the children including extraordinary travel expenses • Extraordinary child care costs required for the
live in the parent’s home or are the subject of when exchanging the child or children for child or children that exceed the maximum state-
a support order, as all children have an equal parenting time wide average cost estimate provided in division
right to share in their parents’ income. • The financial resources and the earning ability (O)(1)(d) of section 3119.05 of the Revised
Parents now receive a standardized of the child or children Code including extraordinary costs associated
deduction from income, instead of a deduction • The relative financial resources, including with caring for a child or children with specified
in the amount of the dependency exemption the disparity in income between parties or physical, psychological, or education needs
less child support received, or child support households, other assets, and the needs of • Any other relevant factor.
paid. The adjustment is the economic cost each parent
of raising the children based on the parent’s • The obligee’s income, if the obligee’s annual Administrative Review of Deviations (R.C.
income per the Schedule. The Schedule income is equal to or less than one hundred per 3119.63)
amount for all children of a parent is divided cent of the federal poverty level Child support agencies may maintain a
by the number of children. The per capita • Benefits that either parent receives from deviation when reviewing a court order if the
amount is then multiplied by the number of remarriage or sharing living expenses with monetary or percentage value of the deviation
children of other relationships. Parents can another person can be unequivocally determined. In the past,
still request a deviation for supporting other • The amount of federal, state, and local taxes parents automatically lost their deviation in an
children, on top of the adjustment. actually paid or estimated to be paid by a agency review. Agencies still cannot establish or
parent or both of the parents modify a deviation.
JULY/AUGUST 2019 CLEVELAND METROPOLITAN BAR JOURNAL | 31