Page 11 - SUBHARADEV SEN AND AHMED
P. 11
IAPQR Transactions
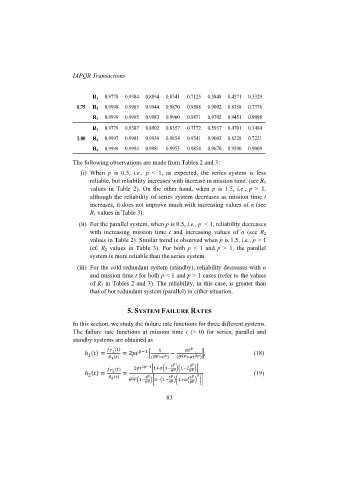
R 1 0.9778 0.9384 0.8894 0.8341 0.7125 0.5848 0.4571 0.3329
0.75 R 2 0.9998 0.9983 0.9944 0.9870 0.9588 0.9092 0.8358 0.7376
R 3 0.9999 0.9995 0.9983 0.9960 0.9871 0.9705 0.9451 0.9098
R 1 0.9779 0.9387 0.8902 0.8357 0.7172 0.5937 0.4701 0.3484
1.00 R 2 0.9997 0.9981 0.9936 0.9854 0.9541 0.9003 0.8228 0.7221
R 3 0.9999 0.9994 0.9981 0.9955 0.9854 0.9670 0.9390 0.9009
The following observations are made from Tables 2 and 3:
(i) When p is 0.5, i.e., p < 1, as expected, the series system is less
reliable, but reliability increases with increase in mission time. (see R 1
values in Table 2). On the other hand, when p is 1.5, i.e., p > 1,
although the reliability of series system decreases as mission time t
increases, it does not improve much with increasing values of α (see
R 1 values in Table 3).
(ii) For the parallel system, when p is 0.5, i.e., p < 1, reliability decreases
with increasing mission time t and increasing values of α (see R 2
values in Table 2). Similar trend is observed when p is 1.5, i.e., p > 1
(cf. R 2 values in Table 3). For both p < 1 and p > 1, the parallel
system is more reliable than the series system.
(iii) For the cold redundant system (standby), reliability decreases with α
and mission time t for both p < 1 and p > 1 cases (refer to the values
of R 3 in Tables 2 and 3). The reliability, in this case, is greater than
that of hot redundant system (parallel) in either situation.
5. SYSTEM FAILURE RATES
In this section, we study the failure rate functions for three different systems.
The failure rate functions at mission time t (> 0) for series, parallel and
standby systems are obtained as
2 , (18)
(19)
83