Page 12 - EIA Report on Tanzanian African Ivory Smuggling 2014 report
P. 12
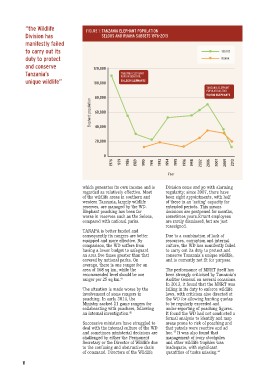
“the Wildlife FIGURE 1: TANZANIA ELEPHANT POPULATION
Division has SELOUS AND RUAHA SUBSETS 1976-2013
manifestly failed
to carry out its 120,000 TANZANIA ELEPHANT SELOUS
duty to protect 100,000 POPULATION 1979: RUAHA
and conserve 80,000
Tanzania’s 60,000 316,300 ELEPHANTS TANZANIA ELEPHANT
unique wildlife” 40,000 POPULATION, 2013:
20,000 50,500 ELEPHANTS
11
Elephant population 0
1976
1979
1986
1989
1990
1991
1993
1994
1995
1996
1998
2002
2006
2007
2009
2013
Year
which generates its own income and is Division come and go with alarming
regarded as relatively effective. Most regularity; since 2007, there have
of the wildlife areas in southern and been eight appointments, with half
western Tanzania, largely wildlife of these in an ‘acting’ capacity for
reserves, are managed by the WD. extended periods. This means
Elephant poaching has been far decisions are postponed for months,
worse in reserves such as the Selous, sometimes years.Errant employees
compared with national parks. are rarely dismissed, but are just
reassigned.
TANAPA is better funded and
consequently its rangers are better Due to a combination of lack of
equipped and more effective. By resources, corruption and internal
comparison, the WD suffers from culture, the WD has manifestly failed
having a lower budget to safeguard to carry out its duty to protect and
an area five times greater than that conserve Tanzania’s unique wildlife,
covered by national parks. On and is currently not fit for purpose.
average, there is one ranger for an
area of 168 sq km, while the The performance of MNRT itself has
recommended level should be one been strongly criticised by Tanzania’s
ranger per 25 sq km.41 Auditor General on several occasions.
In 2013, it found that the MNRT was
The situation is made worse by the failing in its duty to enforce wildlife
involvement of some rangers in laws, with criticism also directed at
poaching. In early 2014, the the WD for allowing hunting quotas
Ministry sacked 21 game rangers for to be regularly exceeded and
collaborating with poachers, following under-reporting of poaching figures.
an internal investigation.42 It found the WD had not conducted a
formal analysis to identify and map
Successive ministers have struggled to areas prone to risk of poaching and
deal with the internal culture of the WD that patrols were reactive and ad
and sometimes ministerial decisions are hoc.43 It was also found that
challenged by either the Permanent management of ivory stockpiles
Secretary or the Director of Wildlife due and other wildlife trophies was
to the confusing and obstructive chain inadequate, with significant
of command. Directors of the Wildlife quantities of tusks missing.44