Page 141 - Building Digital Libraries
P. 141
CHAPTER 6
was removed from the sample record. At present, Unqualified Dublin Core
defines the following fifteen elements: 13
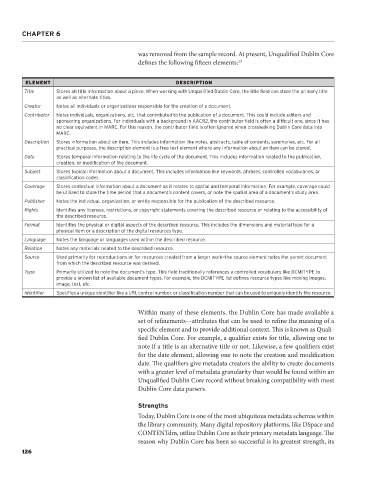
ELEMENT DESCRIPTION
Title Stores all title information about a piece. When working with Unqualified Dublin Core, the title field can store the primary title
as well as alternate titles.
Creator Notes all individuals or organizations responsible for the creation of a document.
Contributor Notes individuals, organizations, etc. that contributed to the publication of a document. This could include editors and
sponsoring organizations. For individuals with a background in AACR2, the contributor field is often a difficult one, since it has
no clear equivalent in MARC. For this reason, the contributor field is often ignored when crosswalking Dublin Core data into
MARC.
Description Stores information about an item. This includes information like notes, abstracts, table of contents, summaries, etc. For all
practical purposes, the description element is a free text element where any information about an item can be stored.
Date Stores temporal information relating to the life cycle of the document. This includes information related to the publication,
creation, or modification of the document.
Subject Stores topical information about a document. This includes information like keywords, phrases, controlled vocabularies, or
classification codes.
Coverage Stores contextual information about a document as it relates to spatial and temporal information. For example, coverage could
be utilized to store the time period that a document’s content covers, or note the spatial area of a document’s study area.
Publisher Notes the individual, organization, or entity responsible for the publication of the described resource.
Rights Identifies any licenses, restrictions, or copyright statements covering the described resource or relating to the accessibility of
the described resource.
Format Identifies the physical or digital aspects of the described resource. This includes the dimensions and material type for a
physical item or a description of the digital resources type.
Language Notes the language or languages used within the described resource.
Relation Notes any materials related to the described resource.
Source Used primarily for reproductions or for resources created from a larger work—the source element notes the parent document
from which the described resource was derived.
Type Primarily utilized to note the document’s type. This field traditionally references a controlled vocabulary like DCMITYPE to
provide a known list of available document types. For example, the DCMITYPE list defines resource types like moving images,
image, text, etc.
Identifier Specifies a unique identifier like a URI, control number, or classification number that can be used to uniquely identify the resource.
Within many of these elements, the Dublin Core has made available a
set of refinements—attributes that can be used to refine the meaning of a
specific element and to provide additional context. This is known as Quali-
fied Dublin Core. For example, a qualifier exists for title, allowing one to
note if a title is an alternative title or not. Likewise, a few qualifiers exist
for the date element, allowing one to note the creation and modification
date. The qualifiers give metadata creators the ability to create documents
with a greater level of metadata granularity than would be found within an
Unqualified Dublin Core record without breaking compatibility with most
Dublin Core data parsers.
Strengths
Today, Dublin Core is one of the most ubiquitous metadata schemas within
the library community. Many digital repository platforms, like DSpace and
CONTENTdm, utilize Dublin Core as their primary metadata language. The
reason why Dublin Core has been so successful is its greatest strength, its
126