Page 41 - JOP2020
P. 41
Ecological Distribution
Acanthamoeba have the ability to
survive in various environments.
They have been found in aquatic
environments including ponds,
stagnant water, freshwater lakes,
rivers, and salt water. They have
also been discovered in bottled
water, distilled water, tap water,
and even in swimming pools and
hot tubs. Acanthamoeba also exist
in compost, soil, and beach sand
and on vegetables. They have been
recovered from contact-lens cases
and solutions, eye-wash stations,
dental-treatment equipment,
air-conditioner units, skin lesions,
dialysis machines, lung-tissue
samples, cerebrospinal fluid, brain
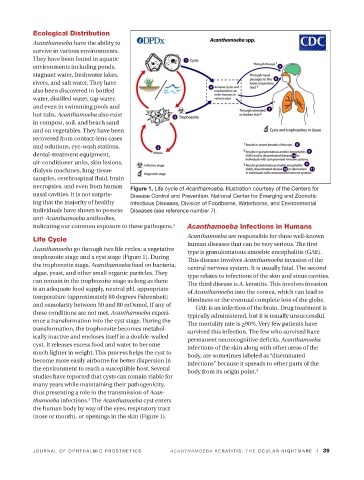
necropsies, and even from human Figure 1. Life cycle of Acanthamoeba. Illustration courtesy of the Centers for
nasal cavities. It is not surpris- Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic
ing that the majority of healthy Infectious Diseases, Division of Foodborne, Waterborne, and Environmental
individuals have shown to possess Diseases (see reference number 7).
anti-Acanthamoeba antibodies,
indicating our common exposure to these pathogens. 3 Acanthamoeba Infections in Humans
Life Cycle Acanthamoeba are responsible for three well-known
human diseases that can be very serious. The first
Acanthamoeba go through two life cycles: a vegetative type is granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE).
trophozoite stage and a cyst stage (Figure 1). During This disease involves Acanthamoeba invasion of the
the trophozoite stage, Acanthamoeba feed on bacteria, central nervous system. It is usually fatal. The second
algae, yeast, and other small organic particles. They type relates to infections of the skin and sinus cavities.
can remain in the trophozoite stage as long as there The third disease is A. keratitis. This involves invasion
is an adequate food supply, neutral pH, appropriate of Acanthamoeba into the cornea, which can lead to
temperature (approximately 80 degrees Fahrenheit) blindness or the eventual complete loss of the globe.
and osmolarity between 50 and 80 mOsmol. If any of GAE is an infection of the brain. Drug treatment is
these conditions are not met, Acanthamoeba experi- typically administered, but it is usually unsuccessful.
ence a transformation into the cyst stage. During the The mortality rate is >90%. Very few patients have
transformation, the trophozoite becomes metabol- survived this infection. The few who survived have
ically inactive and encloses itself in a double-walled permanent neurocognitive deficits. Acanthamoeba
cyst. It releases excess food and water to become infections of the skin along with other areas of the
much lighter in weight. This process helps the cyst to body, are sometimes labeled as “diseminated
become more easily airborne for better dispersion in infections” because it spreads to other parts of the
the environment to reach a susceptible host. Several body from its origin point. 2
studies have reported that cysts can remain viable for
many years while maintaining their pathogenicity,
thus presenting a role in the transmission of Acan-
3
thamoeba infections. The Acanthamoeba cyst enters
the human body by way of the eyes, respiratory tract
(nose or mouth), or openings in the skin (Figure 1).
JOURNAL OF OPHTHALMIC PROSTHETICS ACANTHAMOEBA KERATITIS: THE OCULAR NIGHTMARE | 39