Page 291 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 291
7. Measuring and reporting inventories
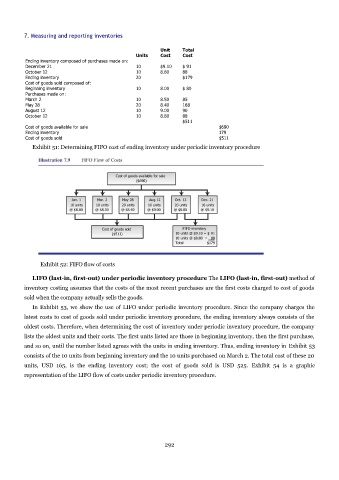
Unit Total
Units Cost Cost
Ending inventory composed of purchases made on:
December 21 10 $9.10 $ 91
October 12 10 8.80 88
Ending inventory 20 $179
Cost of goods sold composed of:
Beginning inventory 10 8.00 $ 80
Purchases made on:
March 2 10 8.50 85
May 28 20 8.40 168
August 12 10 9.00 90
October 12 10 8.80 88
$511
Cost of goods available for sale $690
Ending inventory 179
Cost of goods sold $511
Exhibit 51: Determining FIFO cost of ending inventory under periodic inventory procedure
Exhibit 52: FIFO flow of costs
LIFO (last-in, first-out) under periodic inventory procedure The LIFO (last-in, first-out) method of
inventory costing assumes that the costs of the most recent purchases are the first costs charged to cost of goods
sold when the company actually sells the goods.
In Exhibit 53, we show the use of LIFO under periodic inventory procedure. Since the company charges the
latest costs to cost of goods sold under periodic inventory procedure, the ending inventory always consists of the
oldest costs. Therefore, when determining the cost of inventory under periodic inventory procedure, the company
lists the oldest units and their costs. The first units listed are those in beginning inventory, then the first purchase,
and so on, until the number listed agrees with the units in ending inventory. Thus, ending inventory in Exhibit 53
consists of the 10 units from beginning inventory and the 10 units purchased on March 2. The total cost of these 20
units, USD 165, is the ending inventory cost; the cost of goods sold is USD 525. Exhibit 54 is a graphic
representation of the LIFO flow of costs under periodic inventory procedure.
292