Page 293 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 293
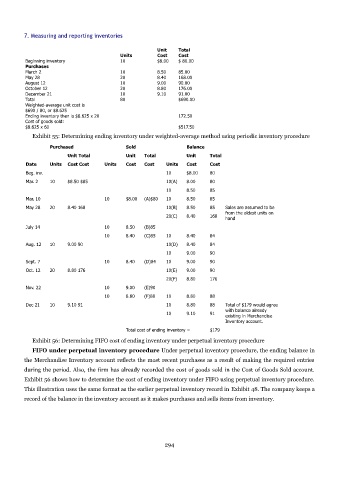
7. Measuring and reporting inventories
Unit Total
Units Cost Cost
Beginning inventory 10 $8.00 $ 80.00
Purchases
March 2 10 8.50 85.00
May 28 20 8.40 168.00
August 12 10 9.00 90.00
October 12 20 8.80 176.00
December 21 10 9.10 91.00
Total 80 $690.00
Weighted-average unit cost is
$690 / 80, or $8.625
Ending inventory then is $8.625 x 20 172.50
Cost of goods sold:
$8.625 x 60 $517.50
Exhibit 55: Determining ending inventory under weighted-average method using periodic inventory procedure
Purchased Sold Balance
Unit Total Unit Total Unit Total
Date Units Cost Cost Units Cost Cost Units Cost Cost
Beg. inv. 10 $8.00 80
Mar. 2 10 $8.50 $85 10(A) 8.00 80
10 8.50 85
Mar. 10 10 $8.00 (A)$80 10 8.50 85
May 28 20 8.40 168 10(B) 8.50 85 Sales are assumed to be
from the oldest units on
20(C) 8.40 168 hand
July 14 10 8.50 (B)85
10 8.40 (C)85 10 8.40 84
Aug. 12 10 9.00 90 10(D) 8.40 84
10 9.00 90
Sept. 7 10 8.40 (D)84 10 9.00 90
Oct. 12 20 8.80 176 10(E) 9.00 90
20(F) 8.80 176
Nov. 22 10 9.00 (E)90
10 8.80 (F)88 10 8.80 88
Dec 21 10 9.10 91 10 8.80 88 Total of $179 would agree
with balance already
10 9.10 91 existing in Merchandise
Inventory account.
Total cost of ending inventory = $179
Exhibit 56: Determining FIFO cost of ending inventory under perpetual inventory procedure
FIFO under perpetual inventory procedure Under perpetual inventory procedure, the ending balance in
the Merchandise Inventory account reflects the most recent purchases as a result of making the required entries
during the period. Also, the firm has already recorded the cost of goods sold in the Cost of Goods Sold account.
Exhibit 56 shows how to determine the cost of ending inventory under FIFO using perpetual inventory procedure.
This illustration uses the same format as the earlier perpetual inventory record in Exhibit 48. The company keeps a
record of the balance in the inventory account as it makes purchases and sells items from inventory.
294