Page 569 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 569
14. Stock investments
stockholder's equity and to establish increased
value of land and goodwill.
Entry 2 is the same as elimination entry 2 in Exhibit 108. Entry 2 eliminates the intercompany loan by debiting
Notes Payable and crediting Notes Receivable for USD 5,000.
After these elimination entries are made, the company consolidates and extends the remaining amounts to the
Consolidated Amounts column. It uses the amounts in this column to prepare the consolidated balance sheet in
Exhibit 110. Notice that the firm carries the USD 15,000 debit to Goodwill to the Consolidated Amounts column
and lists it as an asset in the consolidated balance sheet.
As noted earlier, a company may purchase all or part of another company at more than book value and create
goodwill on the consolidated balance sheet. FASB Statement No. 142 (2001) requires goodwill to be recorded at
acquisition cost and to remain at this amount until there is evidence of impairment. We leave a discussion of this
topic to a more advanced text.
Under some circumstances, a parent company may pay less than book value of the subsidiary's net assets. In
such cases, it is highly unlikely that a bargain purchase has been made. The most logical explanation is that some of
the subsidiary's assets are overvalued. Firms use the excess of book value over cost to reduce proportionately the
value of the noncurrent assets acquired (except long-term investments in marketable securities). If noncurrent
assets are reduced to zero, the remaining dollar amount is a deferred credit entitled, Excess of Fair Value Over Cost
of Assets Acquired.
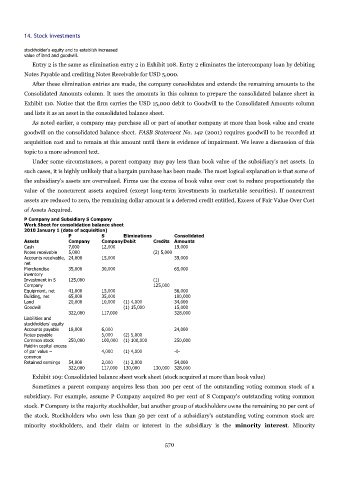
P Company and Subsidiary S Company
Work Sheet for consolidation balance sheet
2010 January 1 (date of acquisition)
P S Eliminations Consolidated
Assets Company CompanyDebit Credits Amounts
Cash 7,000 12,000 19,000
Notes receivable 5,000 (2) 5,000
Accounts receivable, 24,000 15,000 39,000
net
Merchandise 35,000 30,000 65,000
inventory
Investment in S 125,000 (1)
Company 125,000
Equipment, net 41,000 15,000 56,000
Building, net 65,000 35,000 100,000
Land 20,000 10,000 (1) 4,000 34,000
Goodwill (1) 15,000 15,000
322,000 117,000 328,000
Liabilities and
stockholders' equity
Accounts payable 18,000 6,000 24,000
Notes payable 5,000 (2) 5,000
Common stock 250,000 100,000 (1) 100,000 250,000
Paid-in capital excess
of par value – 4,000 (1) 4,000 -0-
common
Retained earnings 54,000 2,000 (1) 2,000 54,000
322,000 117,000 130,000 130,000 328,000
Exhibit 109: Consolidated balance sheet work sheet (stock acquired at more than book value)
Sometimes a parent company acquires less than 100 per cent of the outstanding voting common stock of a
subsidiary. For example, assume P Company acquired 80 per cent of S Company's outstanding voting common
stock. P Company is the majority stockholder, but another group of stockholders owns the remaining 20 per cent of
the stock. Stockholders who own less than 50 per cent of a subsidiary's outstanding voting common stock are
minority stockholders, and their claim or interest in the subsidiary is the minority interest. Minority
570