Page 901 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 901
23. Budgeting for planning and control
• Supporting budgets also may be developed for accounts receivable, inventories, accounts affected by
operating costs, and federal income taxes payable.
Demonstration problem
During January 2010, Ramos Company plans to sell 40,000 units of its product at a price of USD 30 per unit.
The company estimates selling expenses to be USD 120,000 plus 2 per cent of sales revenue. Administrative
expenses are estimated to be USD 90,000 plus 1 per cent of sales revenue. Federal income tax expense is estimated
to be 40 per cent of income before federal income taxes.
Ramos plans to produce 50,000 units during January with estimated variable costs per unit as follows: USD 3
for material, USD 7.50 for labor, and USD 4.50 for variable overhead. Estimated fixed overhead cost is USD 60,000
per month. The finished goods inventory at 2010 January 1, is 8,000 units with a cost per unit of USD 15. The
company uses FIFO inventory procedure.
Prepare a projected income statement for January 2010.
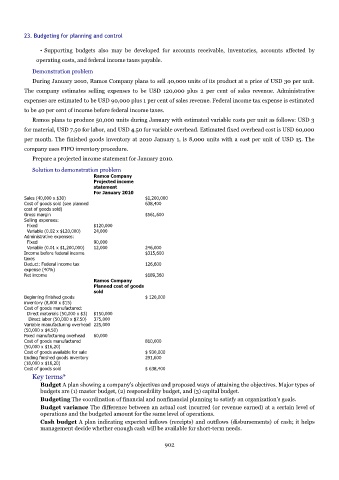
Solution to demonstration problem
Ramos Company
Projected income
statement
For January 2010
Sales (40,000 x $30) $1,200,000
Cost of goods sold (see planned 638,400
cost of goods sold)
Gross margin $561,600
Selling expenses:
Fixed $120,000
Variable (0.02 x $120,000) 24,000
Administrative expenses:
Fixed 90,000
Variable (0.01 x $1,200,000) 12,000 246,000
Income before federal income $315,600
taxes
Deduct: Federal income tax 126,600
expense (40%)
Net income $189,360
Ramos Company
Planned cost of goods
sold
Beginning finished goods $ 120,000
inventory (8,000 x $15)
Cost of goods manufactured:
Direct materials (50,000 x $3) $150,000
Direct labor (50,000 x $7.50) 375,000
Variable manufacturing overhead 225,000
(50,000 x $4.50)
Fixed manufacturing overhead 60,000
Cost of goods manufactured 810,000
(50,000 x $16,20)
Cost of goods available for sale $ 930,000
Ending finished goods inventory 291,600
(18,000 x $16,20)
Cost of goods sold $ 638,400
Key terms*
Budget A plan showing a company's objectives and proposed ways of attaining the objectives. Major types of
budgets are (1) master budget, (2) responsibility budget, and (3) capital budget.
Budgeting The coordination of financial and nonfinancial planning to satisfy an organization's goals.
Budget variance The difference between an actual cost incurred (or revenue earned) at a certain level of
operations and the budgeted amount for the same level of operations.
Cash budget A plan indicating expected inflows (receipts) and outflows (disbursements) of cash; it helps
management decide whether enough cash will be available for short-term needs.
902