Page 41 - PowerPoint 演示文稿
P. 41
Spherical Lenses 31
Fig. 3.7: Prismatic deviation by spherical lenses
DETECTION OF SPHERICAL LENS
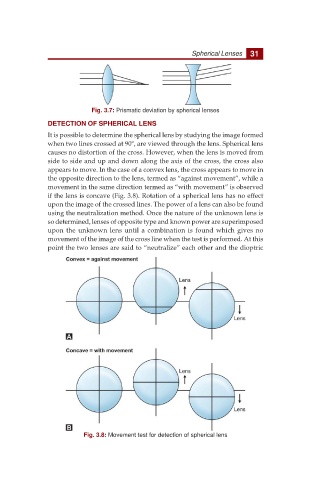
It is possible to determine the spherical lens by studying the image formed
when two lines crossed at 90º, are viewed through the lens. Spherical lens
causes no distortion of the cross. However, when the lens is moved from
side to side and up and down along the axis of the cross, the cross also
appears to move. In the case of a convex lens, the cross appears to move in
the opposite direction to the lens, termed as “against movement”, while a
movement in the same direction termed as “with movement” is observed
if the lens is concave (Fig. 3.8). Rotation of a spherical lens has no effect
upon the image of the crossed lines. The power of a lens can also be found
using the neutralization method. Once the nature of the unknown lens is
so determined, lenses of opposite type and known power are superimposed
upon the unknown lens until a combination is found which gives no
movement of the image of the cross line when the test is performed. At this
point the two lenses are said to “neutralize” each other and the dioptric
Fig. 3.8: Movement test for detection of spherical lens