Page 75 - NAME OF CONDITION: REFRACTIVE ERRORS
P. 75
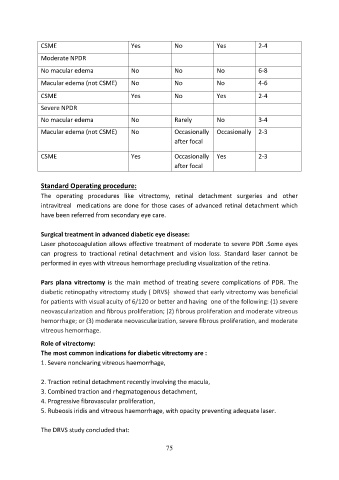
CSME Yes No Yes 2-4
Moderate NPDR
No macular edema No No No 6-8
Macular edema (not CSME) No No No 4-6
CSME Yes No Yes 2-4
Severe NPDR
No macular edema No Rarely No 3-4
Macular edema (not CSME) No Occasionally Occasionally 2-3
after focal
CSME Yes Occasionally Yes 2-3
after focal
Standard Operating procedure:
The operating procedures like vitrectomy, retinal detachment surgeries and other
intravitreal medications are done for those cases of advanced retinal detachment which
have been referred from secondary eye care.
Surgical treatment in advanced diabetic eye disease:
Laser photocoagulation allows effective treatment of moderate to severe PDR .Some eyes
can progress to tractional retinal detachment and vision loss. Standard laser cannot be
performed in eyes with vitreous hemorrhage precluding visualization of the retina.
Pars plana vitrectomy is the main method of treating severe complications of PDR. The
diabetic retinopathy vitrectomy study ( DRVS) showed that early vitrectomy was beneficial
for patients with visual acuity of 6/120 or better and having one of the following: (1) severe
neovascularization and fibrous proliferation; (2) fibrous proliferation and moderate vitreous
hemorrhage; or (3) moderate neovascularization, severe fibrous proliferation, and moderate
vitreous hemorrhage.
Role of vitrectomy:
The most common indications for diabetic vitrectomy are :
1. Severe nonclearing vitreous haemorrhage,
2. Traction retinal detachment recently involving the macula,
3. Combined traction and rhegmatogenous detachment,
4. Progressive fibrovascular proliferation,
5. Rubeosis iridis and vitreous haemorrhage, with opacity preventing adequate laser.
The DRVS study concluded that:
75