Page 67 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 67
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
T3 CAMPUS
Department of Information Technology DCIT 25 – Data Structures and Algorithms
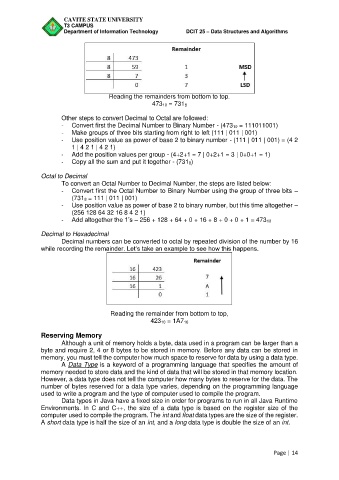
Reading the remainders from bottom to top.
47310 = 7318
Other steps to convert Decimal to Octal are followed:
- Convert first the Decimal Number to Binary Number - (47310 = 111011001)
- Make groups of three bits starting from right to left (111 | 011 | 001)
- Use position value as power of base 2 to binary number - (111 | 011 | 001) = (4 2
1 | 4 2 1 | 4 2 1)
- Add the position values per group - (4+2+1 = 7 | 0+2+1 = 3 | 0+0+1 = 1)
- Copy all the sum and put it together - (7318)
Octal to Decimal
To convert an Octal Number to Decimal Number, the steps are listed below:
- Convert first the Octal Number to Binary Number using the group of three bits –
(7318 = 111 | 011 | 001)
- Use position value as power of base 2 to binary number, but this time altogether –
(256 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1)
- Add altogether the 1’s – 256 + 128 + 64 + 0 + 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 473 10
Decimal to Hexadecimal
Decimal numbers can be converted to octal by repeated division of the number by 16
while recording the remainder. Let’s take an example to see how this happens.
Reading the remainder from bottom to top,
42310 = 1A716
Reserving Memory
Although a unit of memory holds a byte, data used in a program can be larger than a
byte and require 2, 4 or 8 bytes to be stored in memory. Before any data can be stored in
memory, you must tell the computer how much space to reserve for data by using a data type.
A Data Type is a keyword of a programming language that specifies the amount of
memory needed to store data and the kind of data that will be stored in that memory location.
However, a data type does not tell the computer how many bytes to reserve for the data. The
number of bytes reserved for a data type varies, depending on the programming language
used to write a program and the type of computer used to compile the program.
Data types in Java have a fixed size in order for programs to run in all Java Runtime
Environments. In C and C++, the size of a data type is based on the register size of the
computer used to compile the program. The int and float data types are the size of the register.
A short data type is half the size of an int, and a long data type is double the size of an int.
Page | 14