Page 71 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 71
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
T3 CAMPUS
Department of Information Technology DCIT 25 – Data Structures and Algorithms
A class definition is a stencil similar in a concept to a structure definition in that both
use the definition to create instances. A structure definition creates an instance of a structure,
while a class definition creates an instance of a class.
A class definition translates attributes and behaviors of a real-life object into a
simulation of that object within a program. Attributes are data elements similar to elements of
a structure. Behaviors are instructions that performs specific tasks known as either methods
or functions.
Defining a Class
A class definition resembles a definition of a structure, as you can see in the following
example. A class definition consists of four elements:
Class – Tells the computer that you are defining a class
Class Name – The name used to uniquely identify the class and used to declare
instances of a class.
Class Body – Open and close braces within which are primitive data types that are
declared when an instance of the class is declared and definitions of methods and
functions that are members of the class.
Semicolon – Tells the computer this is an instruction (statement)
The following class definition written in C++ defines the same student record that is
defined in the structure. However, the class definition also defines a function that displays the
student number and grade on the screen.
class StudentRecord {
int studentNumber;
char grade;
void displayGrade() {
cout << “Student Number: “ << studentNumber << endl;
cout << “Student Grade: “ <<grade << endl;
}
};
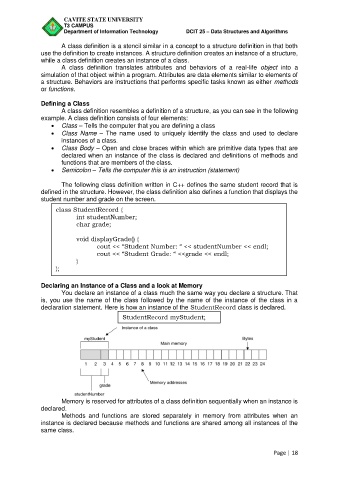
Declaring an Instance of a Class and a look at Memory
You declare an instance of a class much the same way you declare a structure. That
is, you use the name of the class followed by the name of the instance of the class in a
declaration statement. Here is how an instance of the StudentRecord class is declared.
StudentRecord myStudent;
Memory is reserved for attributes of a class definition sequentially when an instance is
declared.
Methods and functions are stored separately in memory from attributes when an
instance is declared because methods and functions are shared among all instances of the
same class.
Page | 18