Page 74 - PowerPoint Presentation
P. 74
CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY
T3 CAMPUS
Department of Information Technology DCIT 25 – Data Structures and Algorithms
Likewise, the int data type of the ptStudentNumber pointer states that the contents
of the memory location associated with ptStudentNumber will contain the address of an
integer variable.
Why does the computer need to know this? For now, let’s simply say that programmers
instruct the computer to manipulate memory addresses using pointer arithmetic. In order for
the computer to carry out those instructions, the computer must know the data type of the
address contained in a pointer. We’ll going to tackle pointer arithmetic later.
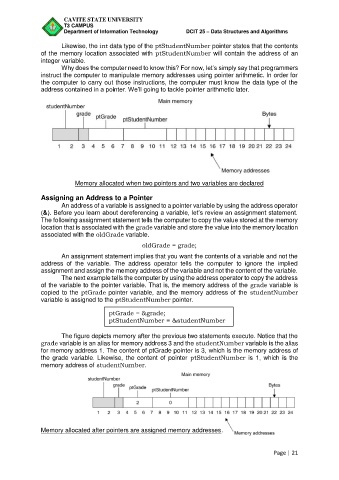
Memory allocated when two pointers and two variables are declared
Assigning an Address to a Pointer
An address of a variable is assigned to a pointer variable by using the address operator
(&). Before you learn about dereferencing a variable, let’s review an assignment statement.
The following assignment statement tells the computer to copy the value stored at the memory
location that is associated with the grade variable and store the value into the memory location
associated with the oldGrade variable.
oldGrade = grade;
An assignment statement implies that you want the contents of a variable and not the
address of the variable. The address operator tells the computer to ignore the implied
assignment and assign the memory address of the variable and not the content of the variable.
The next example tells the computer by using the address operator to copy the address
of the variable to the pointer variable. That is, the memory address of the grade variable is
copied to the ptGrade pointer variable, and the memory address of the studentNumber
variable is assigned to the ptStudentNumber pointer.
ptGrade = &grade;
ptStudentNumber = &studentNumber
The figure depicts memory after the previous two statements execute. Notice that the
grade variable is an alias for memory address 3 and the studentNumber variable is the alias
for memory address 1. The content of ptGrade pointer is 3, which is the memory address of
the grade variable. Likewise, the content of pointer ptStudentNumber is 1, which is the
memory address of studentNumber.
Memory allocated after pointers are assigned memory addresses.
Page | 21