Page 18 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 18
8 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
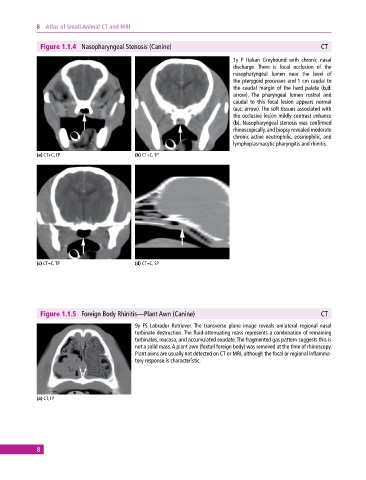
Figure 1.1.4 Nasopharyngeal Stenosis (Canine) CT
1y F Italian Greyhound with chronic nasal
discharge. There is focal occlusion of the
nasopharyngeal lumen near the level of
the pterygoid processes and 1 cm caudal to
the caudal margin of the hard palate (b,d:
arrow). The pharyngeal lumen rostral and
caudal to this focal lesion appears normal
(a,c: arrow). The soft tissues associated with
the occlusive lesion mildly contrast enhance
(b). Nasopharyngeal stenosis was confirmed
rhinoscopically, and biopsy revealed moderate
chronic active neutrophilic, eosinophilic, and
lymphoplasmacytic pharyngitis and rhinitis.
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, SP
Figure 1.1.5 Foreign Body Rhinitis—Plant Awn (Canine) CT
9y FS Labrador Retriever. The transverse plane image reveals unilateral regional nasal
turbinate destruction. The fluid‐attenuating mass represents a combination of remaining
turbinates, mucosa, and accumulated exudate. The fragmented gas pattern suggests this is
not a solid mass. A plant awn (foxtail foreign body) was removed at the time of rhinoscopy.
Plant awns are usually not detected on CT or MRI, although the focal or regional inflamma-
tory response is characteristic.
(a) CT, TP
8