Page 32 - SSAB Welding Handbook Edition 2
P. 32
©2009-2019 by SSAB Group of companies (SSAB). All rights reserved. Only digital PDF file. No distribution. No printing allowed!
No part of this handbook may be reproduced in any form or by any means without permission in writing from SSAB.
5.0 Properties of the heat-affected zone Welding handbook
©SSAB
1600
Time [s]
1400 The coarsed grained zone
Temperature [°C] 1000 The fine grained zone
1200
The partially transformed zone
The annealed zone
800
600
400
200
0
0 5 10 15202530 354045 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115
Tid [s]
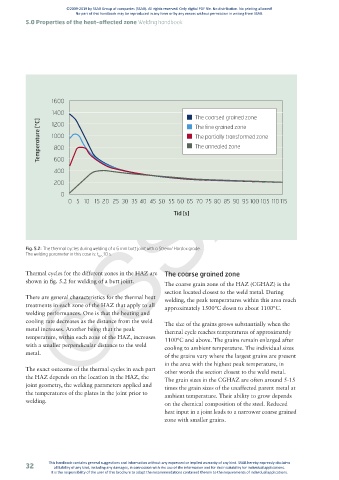
Fig. 5.2: The thermal cycles during welding of a 6 mm butt joint with a Strenx/ Hardox grade.
The welding parameter in this case is: t :10 s.
8/5
Thermal cycles for the different zones in the HAZ are The coarse grained zone
shown in fig. 5.2 for welding of a butt joint. The coarse grain zone of the HAZ (CGHAZ) is the
section located closest to the weld metal. During
There are general characteristics for the thermal heat welding, the peak temperatures within this area reach
treatments in each zone of the HAZ that apply to all approximately 1500°C down to about 1100°C.
welding performances. One is that the heating and
cooling rate decreases as the distance from the weld The size of the grains grows substantially when the
metal increases. Another being that the peak thermal cycle reaches temperatures of approximately
temperature, within each zone of the HAZ, increases 1100ºC and above. The grains remain enlarged after
with a smaller perpendicular distance to the weld cooling to ambient temperature. The individual sizes
metal.
of the grains vary where the largest grains are present
in the area with the highest peak temperature, in
The exact outcome of the thermal cycles in each part other words the section closest to the weld metal.
the HAZ depends on the location in the HAZ, the The grain sizes in the CGHAZ are often around 5-15
joint geometry, the welding parameters applied and times the grain sizes of the unaffected parent metal at
the temperatures of the plates in the joint prior to ambient temperature. Their ability to grow depends
welding.
on the chemical composition of the steel. Reduced
heat input in a joint leads to a narrower coarse grained
zone with smaller grains.
32 This handbook contains general suggestions and information without any expressed or implied warranty of any kind. SSAB hereby expressly disclaims
all liability of any kind, including any damages, in connection with the use of the information and for their suitability for individual applications.
It is the responsibility of the user of this brochure to adapt the recommendations contained therein to the requirements of individual applications.