Page 29 - Ebook Digestive System Grade XI
P. 29
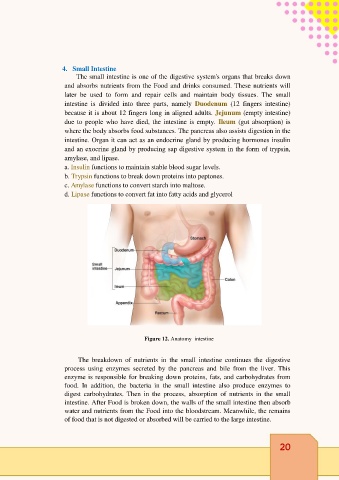
4. Small Intestine
The small intestine is one of the digestive system's organs that breaks down
and absorbs nutrients from the Food and drinks consumed. These nutrients will
later be used to form and repair cells and maintain body tissues. The small
intestine is divided into three parts, namely Duodenum (12 fingers intestine)
because it is about 12 fingers long in aligned adults. Jejunum (empty intestine)
due to people who have died, the intestine is empty. Ileum (gut absorption) is
where the body absorbs food substances. The pancreas also assists digestion in the
intestine. Organ it can act as an endocrine gland by producing hormones insulin
and an exocrine gland by producing sap digestive system in the form of trypsin,
amylase, and lipase.
a. Insulin functions to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
b. Trypsin functions to break down proteins into peptones.
c. Amylase functions to convert starch into maltose.
d. Lipase functions to convert fat into fatty acids and glycerol
Figure 12. Anatomy intestine
The breakdown of nutrients in the small intestine continues the digestive
process using enzymes secreted by the pancreas and bile from the liver. This
enzyme is responsible for breaking down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates from
food. In addition, the bacteria in the small intestine also produce enzymes to
digest carbohydrates. Then in the process, absorption of nutrients in the small
intestine. After Food is broken down, the walls of the small intestine then absorb
water and nutrients from the Food into the bloodstream. Meanwhile, the remains
of food that is not digested or absorbed will be carried to the large intestine.
20