Page 33 - NEA NEWHERE FLIPBOOK
P. 33
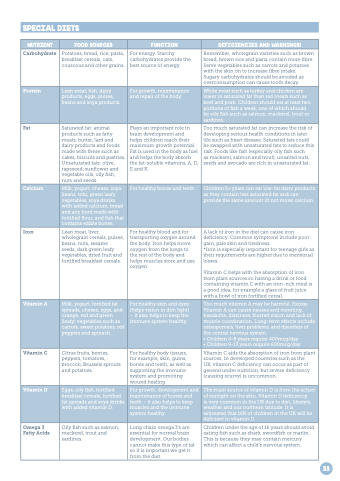
SPECIAL DIETS
NUTRIENT FOOD SOURCES FUNCTION DEFICIENCIES AND WARNINGS!
Carbohydrate
Potatoes bread rice pasta breakfast cereals oats couscous and other grains For energy Starchy carbohydrates provide the best source of energy Remember wholegrain varieties such as brown bread brown rice and pasta contain more fibre Serve vegetables such as carrots and potatoes with the skin on to increase fibre intake Sugary carbohydrates should be avoided as overconsumption can cause tooth decay Protein
Lean meat fish dairy products eggs pulses beans and soya products For growth maintenance and repair of the body White meat such as turkey and chicken are lower in saturated fat than red meats such as beef and pork Children should eat at at least two portions of of fish a week one of of which should be oily fish such as salmon mackerel trout or sardines Fat
Saturated fat: animal products such as fatty meats butter lard and dairy products and foods made with these such as cakes biscuits and pastries Unsaturated fats: olive rapeseed sunflower and vegetable oils oily fish nuts and seeds Plays an an important role in brain development and helps children reach their maximum growth potential Fat
is used in the body as fuel and helps the body absorb the fat-soluble vitamins A D E and K Too much saturated fat can increase the risk of developing serious health conditions in in later life such as as heart disease Saturated fats could be swapped with unsaturated fats to reduce this risk Foods like fish fish (especially oily fish fish such as mackerel salmon and trout) unsalted nuts seeds and avocado are rich in unsaturated fat Calcium
Milk yogurt cheese soya beans tofu green leafy vegetables soya drinks with added calcium bread and any food made with fortified flour and fish that contains edible bones For healthy bones and teeth Children 5+ years can eat low-fat dairy products as they contain less saturated fat and can provide the same amount (if not more) calcium Iron
Lean meat liver wholegrain cereals pulses beans nuts sesame
seeds dark green leafy vegetables dried fruit and fortified breakfast cereals For healthy blood and for transporting oxygen around the body Iron
helps move oxygen from the lungs to the the rest of the the body and helps muscles store and use oxygen A lack of iron iron in the diet can cause iron iron deficiency Common symptoms include poor gain pale skin and tiredness *Iron is especially important for teenage girls as their requirements are higher due to menstrual losses Vitamin C helps with the absorption of iron from plant sources so so having a a a drink or food containing vitamin C with an iron-rich meal is a a a a a good idea for example a a a a a glass of fruit juice with a a bowl of iron fortified cereal Vitamin A Milk yogurt fortified fat spreads cheese eggs and orange red and green (leafy) vegetables such as carrots sweet potatoes red peppers and spinach For healthy skin and eyes (helps vision in dim light) – it also helps to keep the immune system healthy Too much vitamin A may be harmful Excess Vitamin A can cause nausea and vomiting headache dizziness blurred vision and lack of muscle coordination Long-term effects include osteoporosis liver problems and disorders of the central nervous system • Children 4-8 years require 400mcg/day • Children 9-13 years require 600mcg/day
Vitamin C Citrus fruits berries peppers tomatoes broccoli Brussels sprouts and potatoes For healthy body tissues for example skin gums bones and teeth as as well as as supporting the immune system and promoting wound healing Vitamin C aids the absorption of iron from plant sources In developed countries such as the UK vitamin C deficiency can occur as part of general under nutrition but severe deficiency (causing scurvy) is uncommon Vitamin D Eggs oily fish fortified breakfast cereals fortified fat spreads and soya drinks with added vitamin D For growth development and maintenance of bones and teeth – it also helps to keep muscles and the immune system healthy The main source of vitamin D is from the action of sunlight on the skin Vitamin D deficiency is very common in the UK due to diet lifestyle weather and our northern latitude It is estimated that 16% of children in the UK will be deficient in in vitamin D Omega 3 Fatty Acids
Oily fish such as salmon mackerel trout and sardines Long chain omega 3’s are essential for normal brain development Our bodies cannot make this type of fat so it it is important we get it it from the diet Children under the age of 16 years should avoid eating fish fish such as shark swordfish or or marlin This is is because they may contain mercury which can affect a a a child’s nervous system 33