Page 12 - YORAM RUDY BOOK FINAL
P. 12
P. 12
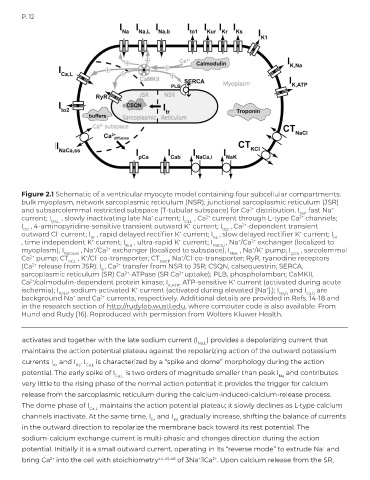
Figure 2.1 Schematic of a ventricular myocyte model containing four subcellular compartments:
bulk myoplasm, network sarcoplasmic reticulum (NSR), junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum (JSR)
and subsarcolemmal restricted subspace (T-tubular subspace) for Ca distribution. I , fast Na
2+
+
Na
current; I Na,L , slowly inactivating late Na current; I Ca,L , Ca current through L-type Ca channels;
2+
+
2+
I , 4-aminopyridine-sensitive transient outward K current; I , Ca -dependent transient
+
2+
t01
t02
outward Cl current; I , rapid delayed rectifier K current; I , slow delayed rectifier K current; I
-
+
+
Kr
Ks
K1
, time independent K current; I Kur , ultra-rapid K current; I NaCa,i , Na /Ca exchanger (localized to
+
+
+
2+
myoplasm); I NaCa,ss , Na /Ca exchanger (localized to subspace); I NaK , Na /K pump; I p,Ca , sarcolemmal
+
+
+
2+
Ca pump; CT KCL , K /Cl co-transporter; CT NaCl , Na /Cl co-transporter; RyR, ryanodine receptors
-
-
2+
+
+
(Ca release from JSR): I , Ca transfer from NSR to JSR; CSQN, calsequestrin; SERCA,
2+
2+
tr
sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca -ATPase (SR Ca uptake); PLB, phospholamban; CaMKII,
2+
2+
Ca /calmodulin-dependent protein kinase; I K,ATP , ATP-sensitive K current (activated during acute
+
2+
ischemia); I K,Na , sodium-activated K current (activated during elevated [Na ] ); I Na,b and I Ca,b are
+
+
i
background Na and Ca currents, respectively. Additional details are provided in Refs. 14-18 and
2+
+
in the research section of http://rudylab.wustl.edu, where computer code is also available. From
Hund and Rudy [16]. Reproduced with permission from Wolters Kluwer Health.
activates and together with the late sodium current (I Na,L ) provides a depolarizing current that
maintains the action potential plateau against the repolarizing action of the outward potassium
currents I and I . I Ca,L is characterized by a “spike and dome” morphology during the action
Kr
Ks
potential. The early spike of I Ca,L is two orders of magnitude smaller than peak I and contributes
Na
very little to the rising phase of the normal action potential; it provides the trigger for calcium
release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum during the calcium-induced-calcium-release process.
The dome phase of I Ca,L maintains the action potential plateau; it slowly declines as L-type calcium
channels inactivate. At the same time, I and I gradually increase, shifting the balance of currents
Ks
Kr
in the outward direction to repolarize the membrane back toward its rest potential. The
sodium-calcium exchange current is multi-phasic and changes direction during the action
potential. Initially it is a small outward current, operating in its “reverse mode” to extrude Na and
+
bring Ca into the cell with stoichiometry 44,45,46 of 3Na :1Ca . Upon calcium release from the SR,
2+
+
2+