Page 136 - YORAM RUDY BOOK FINAL
P. 136
P. 136
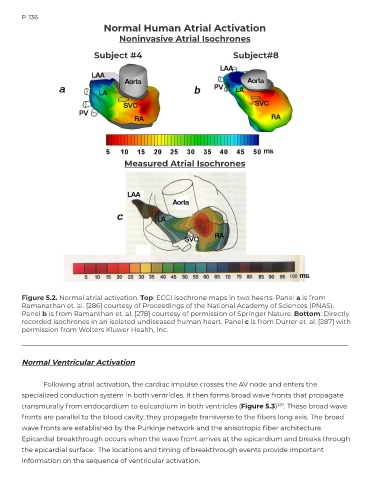
Normal Human Atrial Activation
Noninvasive Atrial Isochrones
Subject #4 Subject#8
Measured Atrial Isochrones
Figure 5.2. Normal atrial activation. Top: ECGI isochrone maps in two hearts. Panel a is from
Ramanathan et. al. [286] courtesy of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Panel b is from Ramanthan et. al. [278] courtesy of permission of Springer Nature. Bottom: Directly
recorded isochrones in an isolated undiseased human heart. Panel c is from Durrer et. al. [287] with
permission from Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Normal Ventricular Activation
Following atrial activation, the cardiac impulse crosses the AV node and enters the
specialized conduction system in both ventricles. It then forms broad wave fronts that propagate
transmurally from endocardium to epicardium in both ventricles (Figure 5.3) 287 . These broad wave
fronts are parallel to the blood cavity; they propagate transverse to the fibers long axis. The broad
wave fronts are established by the Purkinje network and the anisotropic fiber architecture.
Epicardial breakthrough occurs when the wave front arrives at the epicardium and breaks through
the epicardial surface. The locations and timing of breakthrough events provide important
information on the sequence of ventricular activation.