Page 141 - YORAM RUDY BOOK FINAL
P. 141
P. 141
Normal Ventricular Repolarization
A. Epicardial Potential Map
Onset of T-wave C. Recovery Time Isochrones
Anterior Diaphragmatic Anterior Posterior
Peak of T-wave D. Activation Recovery Intervals (ARI)
B. Electrograms
7 SUBJECTS
Mean ARI=235 ms
Mean LV
apex-to-base
ARI dispersion=37 ms
DARI=40 ms
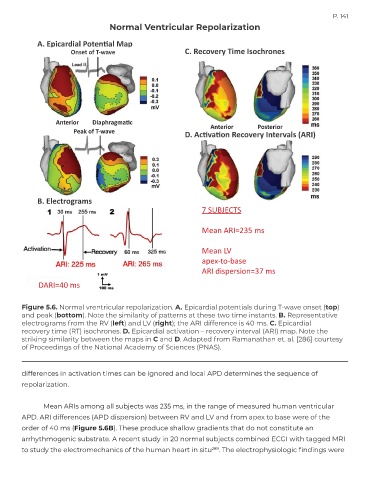
Figure 5.6. Normal vrentricular repolarization. A. Epicardial potentials during T-wave onset (top)
and peak (bottom). Note the similarity of patterns at these two time instants. B. Representative
electrograms from the RV (left) and LV (right); the ARI difference is 40 ms. C. Epicardial
recovery time (RT) isochrones. D. Epicardial activation – recovery interval (ARI) map. Note the
striking similarity between the maps in C and D. Adapted from Ramanathan et. al. [286] courtesy
of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
differences in activation times can be ignored and local APD determines the sequence of
repolarization.
Mean ARIs among all subjects was 235 ms, in the range of measured human ventricular
APD. ARI differences (APD dispersion) between RV and LV and from apex to base were of the
order of 40 ms (Figure 5.6B). These produce shallow gradients that do not constitute an
arrhythmogenic substrate. A recent study in 20 normal subjects combined ECGI with tagged MRI
to study the electromechanics of the human heart in situ 289 . The electrophysiologic findings were