Page 143 - YORAM RUDY BOOK FINAL
P. 143
P. 143
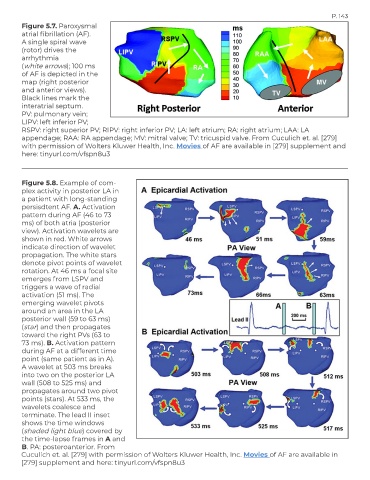
Figure 5.7. Paroxysmal
atrial fibrillation (AF).
A single spiral wave
(rotor) drives the
arrhythmia
(white arrows); 100 ms
of AF is depicted in the
map (right posterior
and anterior views).
Black lines mark the
interatrial septum.
PV: pulmonary vein;
LIPV: left inferior PV;
RSPV: right superior PV; RIPV: right inferior PV; LA: left atrium; RA: right atrium; LAA: LA
appendage; RAA: RA appendage; MV: mitral valve; TV: tricuspid valve. From Cuculich et. al. [279]
with permission of Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Movies of AF are available in [279] supplement and
here: tinyurl.com/vfspn8u3
Figure 5.8. Example of com-
plex activity in posterior LA in
a patient with long-standing
persisdtent AF. A. Activation
pattern during AF (46 to 73
ms) of both atria (posterior
view). Activation wavelets are
shown in red. White arrows
indicate direction of wavelet
propagation. The white stars
denote pivot points of wavelet
rotation. At 46 ms a focal site
emerges from LSPV and
triggers a wave of radial
activation (51 ms). The
emerging wavelet pivots
around an area in the LA
posterior wall (59 to 63 ms)
(star) and then propagates
toward the right PVs (63 to
73 ms). B. Activation pattern
during AF at a different time
point (same patient as in A).
A wavelet at 503 ms breaks
into two on the posterior LA
wall (508 to 525 ms) and
propagates around two pivot
points (stars). At 533 ms, the
wavelets coalesce and
terminate. The lead II inset
shows the time windows
(shaded light blue) covered by
the time-lapse frames in A and
B. PA: posteroanterior. From
Cuculich et. al. [279] with permission of Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Movies of AF are available in
[279] supplement and here: tinyurl.com/vfspn8u3