Page 129 - Demo 1
P. 129
There are two types of respiraon: (1) aerobic respiraon, which requires
oxygen and releases lots of energy, and (2) anaerobic respiraon, which does
not require oxygen and releases much less energy. Aerobic respiraon and
anaerobic respiraon are carried out at the cellular level.
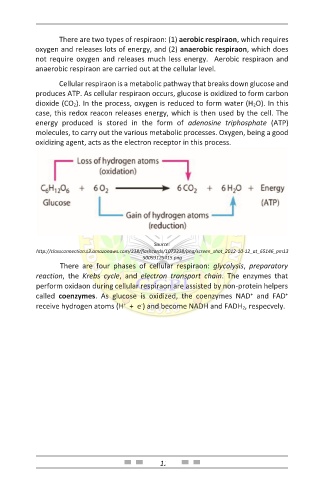
Cellular respiraon is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and
produces ATP. As cellular respiraon occurs, glucose is oxidized to form carbon
dioxide (CO2). In the process, oxygen is reduced to form water (H2O). In this
case, this redox reacon releases energy, which is then used by the cell. The
energy produced is stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
molecules, to carry out the various metabolic processes. Oxygen, being a good
oxidizing agent, acts as the electron receptor in this process.
Source:
http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/338/flashcards/1073338/png/screen_shot_2012-10-12_at_65146_pm13
50093125415.png
There are four phases of cellular respiraon: glycolysis, preparatory
reaction, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain. The enzymes that
perform oxidaon during cellular respiraon are assisted by non-protein helpers
+
+
called coenzymes. As glucose is oxidized, the coenzymes NAD and FAD
+
-
receive hydrogen atoms (H + e ) and become NADH and FADH2, respecvely.
121