Page 24 - Demo 1
P. 24
Ground Tissue
Ground ssue forms the internal bulk of leaves, stems, and roots. It
consists of three types of cells: parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma cells are found in all organs of the plant. These cells are
the least specialized of the cell types; however, they are the cells that carry
out important life processes such as
photosynthesis and cellular respiraon,
including food and water storage.
Parenchyma cells make up the edible
parts of most fruits and vegetables.
Unlike some other cell types,
parenchyma cells remain alive at
maturity with a fully funconal
cytoplasm and a nucleus. They are
capable of cell division and are essenal
to cell regeneraon and wound healing.
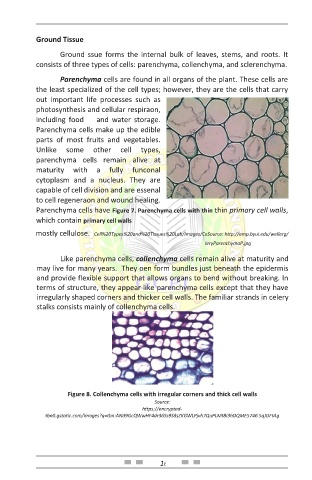
Parenchyma cells have Figure 7. Parenchyma cells with thin thin primary cell walls,
which contain primary cell walls
mostly cellulose. Cell%20Types%20and%20Tissues%20Lab/Images/CeSource: http://emp.byui.edu/wellerg/
leryParenchymaP.jpg
Like parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells remain alive at maturity and
may live for many years. They oen form bundles just beneath the epidermis
and provide flexible support that allows organs to bend without breaking. In
terms of structure, they appear like parenchyma cells except that they have
irregularly shaped corners and thicker cell walls. The familiar strands in celery
stalks consists mainly of collenchyma cells.
Figure 8. Collenchyma cells with irregular corners and thick cell walls
Source:
https://encrypted-
tbn0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQWwHF4dr36Ss9S8sZKGWLPjvh7QuPLMt8i3hDQME5746 5qJDFtAg
16