Page 6 - QR-SLE-8_5_24
P. 6
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
TREATMENT CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
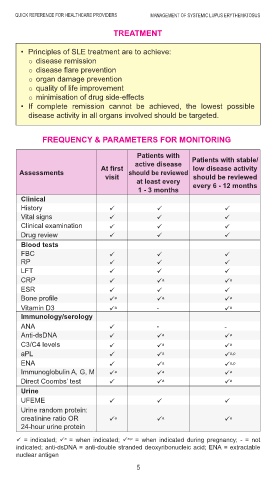
• Principles of SLE treatment are to achieve: Neuropsychiatry
disease remission • Polyneuropathy • Acute confusion state
disease flare prevention • Cerebrovascular • Headache/Migraine
organ damage prevention disease/Stroke • Transverse myelitis
• Cognitive impairment
• Seizure
quality of life improvement • Psychosis
minimisation of drug side-effects Mucocutaneous
• Malar rash
• If complete remission cannot be achieved, the lowest possible • Oral ulcers Eye
disease activity in all organs involved should be targeted. • Photosensitivity • Dry eyes
• Discoid rash • Retinal vasculitis
• Alopecia • Optic neuritis
FREQUENCY & PARAMETERS FOR MONITORING Cardio-respiratory
• ILD Haematology
Patients with • Pericarditis • Leukopenia
active disease Patients with stable/ • PAH • Thrombocytopenia
At first low disease activity • Pleurisy • AIHA
Assessments should be reviewed
visit should be reviewed • Serositis • Lymphopenia
at least every every 6 - 12 months • Myocarditis • APS
1 - 3 months • Libman-Sacks
Clinical endocarditis
History Renal Gastrointestinal
Vital signs • Proteinuria • Pancreatitis
Clinical examination • Microscopic • Enteritis
Drug review haematuria • Lupoid hepatitis
Blood tests
FBC • Raynaud’s
RP Vasculitis phenomenon
LFT
CRP a a
ESR Musculoskeletal
• Arthritis/Arthralgia
Bone profile a a a Constitutional • Myositis
Vitamin D3 a - a symptoms
• Fever
Immunology/serology • Fatigue
ANA - - • Weight loss
Anti-dsDNA a a
C3/C4 levels a a
aPL a a,p
ENA a a,p
Immunoglobulin A, G, M a a a AIHA = autoimmune haemolytic anaemia; APS = antiphospholipid syndrome; ILD =
Direct Coombs’ test a a interstitial lung disease; PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension
Urine
UFEME
Urine random protein:
creatinine ratio OR a a a
24-hour urine protein
= indicated; = when indicated; = when indicated during pregnancy; - = not
a,p
a
indicated; anti-dsDNA = anti-double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid; ENA = extractable
nuclear antigen
5 2