Page 2 - (1-1)eng
P. 2
Elly fat mn 3omry ( 1 – 1 )
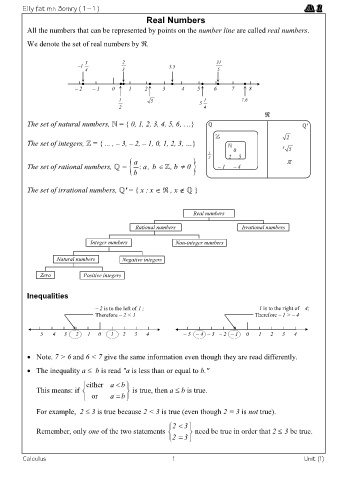
Real Numbers
All the numbers that can be represented by points on the number line are called real numbers.
We denote the set of real numbers by .
3 2 31
1 3.5
4 3 5
– 2 – 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 5 5 1 7.6
2 4
The set of natural numbers, = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, …} '
2
The set of integers, = { ... , – 3, – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …} 1 0 3 5
a 2 2 5
b
a
The set of rational numbers, = b : , b 0 – 1 – 4
,
The set of irrational numbers, ' = { x : x , x }
Real numbers
Rational numbers Irrational numbers
Integer numbers Non-integer numbers
numbers numbers
Natural numbers Negative integers
numbers
Zero Positive integers
numbers
Inequalities
– 2 is to the left of 1 ; – 1 is to the right of – 4;
Therefore – 2 < 1 Therefore – 1 > – 4
– 5 – 4 – 3 – 2 – 1 0 1 2 3 4 – 5 – 4 – 3 – 2 – 1 0 1 2 3 4
Note. 7 > 6 and 6 < 7 give the same information even though they are read differently.
The inequality a b is read "a is less than or equal to b."
either a b
This means: if is true, then a b is true.
or a b
For example, 2 3 is true because 2 < 3 is true (even though 2 = 3 is not true).
2
3
Remember, only one of the two statements need be true in order that 2 3 be true.
2 3
Calculus 1 Unit (1)