Page 5 - (1-1)eng
P. 5
Elly fat mn 3omry ( 1 – 1 )
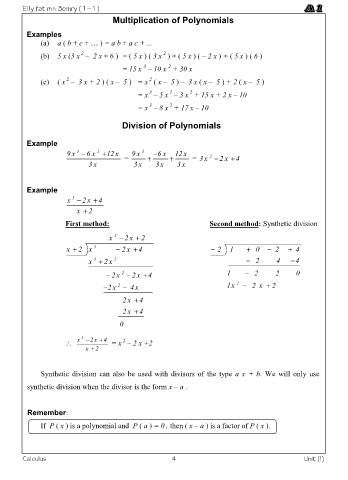
Multiplication of Polynomials
Examples
(a) a ( b + c + … ) = a b + a c + ...
2
2
(b) 5 x (3 x – 2 x + 6 ) = ( 5 x ) ( 3 x ) + ( 5 x ) ( – 2 x ) + ( 5 x ) ( 6 )
3
2
= 15 x – 10 x + 30 x
2
2
(c) ( x – 3 x + 2 ) ( x – 5 ) = x ( x – 5 ) – 3 x ( x – 5 ) + 2 ( x – 5 )
2
3
2
= x – 5 x – 3 x + 15 x + 2 x – 10
3
2
= x – 8 x + 17 x – 10
Division of Polynomials
Example
3
2
9 x 6 x 12 x = 9 x 3 6 x 12 x = 3x 2 x
2
4
3x 3x 3x 3x
Example
x 2 x 4
3
x 2
First method: Second method: Synthetic division
x 2 x 2
2
x 2 x 3 2 x 4 2 1 0 2 4
x 2 x 2 2 4 4
3
2
2 x 2 x 4 1 2 2 0
2 x 4 x 1x 2 2 x 2
2
2 x 4
2 x 4
0
3
x 2 x 4
2
= x – 2 x +2
x 2
Synthetic division can also be used with divisors of the type a x + b. We will only use
synthetic division when the divisor is the form x – a .
Remember:
If P ( x ) is a polynomial and P ( a ) = 0 , then ( x – a ) is a factor of P ( x ).
Calculus 4 Unit (1)