Page 364 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 364
Ionizing Radiation in Veterinary Medicine Chapter | 19 331
VetBooks.ir that is lethal to 50% of the population within 30 days. resistant to total-body radiation doses that are lethal for
other mammals, and cattle have a delayed hematopoietic
LD 50/30 values for six domestic mammal species are sum-
response. The main feature of ARS in swine is severe
marized in Table 19.2. Similar data has been published
for effective radiation doses (Berger et al., 1987). Acute hemorrhage. Breed differences have been documented in
whole-body exposures of .20 Sv are fatal within minutes pigs, with Hampshires surviving 57 days of daily 1 Gy
60
to hours, 5 20 Sv produces symptoms within minutes to doses of Co, compared to 19 days for Yorkshires
hours and death within approximately 1 week, and ,5Sv (Brown et al., 1964). ARS in dogs most similarly resem-
results in hematopoietic effects developing over days to bles what occurs in humans (Tempel, 1983). Minipigs
weeks with death more probably at doses .3 Sv. Mild have been developed as a highly sensitive model for
symptoms may occur with 0.5 1 Sv and ,0.5 Sv is not studying ARS and potential countermeasures (Elliott
et al., 2014). Gamma radiation doses ,2 Gy are lethal
expected to produce any early effects. An estimated LD 50
for humans and several animal species is 3.5 Sv. due to hematopoietic ARS (H-ARS). 2 5 Gy are associ-
In general, as the severity of exposure increases, so ated with an accelerated hematopoietic syndrome.
does the severity of clinical signs and the time of onset 5 12 Gy produces the classic signs of gastrointestinal
decreases, with some differences among animal species ARS (GI-ARS): vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping,
(von Zallinger and Tempel, 1998). Burros are relatively bacterial translocation, and decreased plasma citrulline
levels, a routine biomarker for gastrointestinal syndrome
(Kaore and Kaore, 2014).
Previous stresses such as high levels of production or
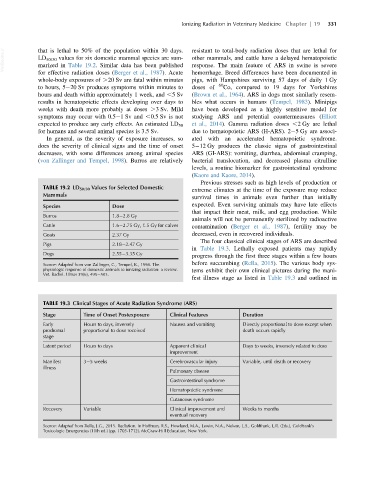
TABLE 19.2 LD 50/30 Values for Selected Domestic
extreme climates at the time of the exposure may reduce
Mammals
survival times in animals even further than initially
Species Dose expected. Even surviving animals may have late effects
that impact their meat, milk, and egg production. While
Burros 1.8 2.8 Gy
animals will not be permanently sterilized by radioactive
Cattle 1.6 2.75 Gy, 1.5 Gy for calves contamination (Berger et al., 1987), fertility may be
Goats 2.37 Gy decreased, even in recovered individuals.
The four classical clinical stages of ARS are described
Pigs 2.18 2.47 Gy
in Table 19.3. Lethally exposed patients may rapidly
Dogs 2.55 3.35 Gy
progress through the first three stages within a few hours
before succumbing (Rella, 2015). The various body sys-
Source: Adapted from von Zallinger, C., Tempel, K., 1998. The
physiologic response of domestic animals to ionizing radiation: a review. tems exhibit their own clinical pictures during the mani-
Vet. Radiol. Ultras 39(6), 495 503.
fest illness stage as listed in Table 19.3 and outlined in
TABLE 19.3 Clinical Stages of Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS)
Stage Time of Onset Postexposure Clinical Features Duration
Early Hours to days, inversely Nausea and vomiting Directly proportional to dose except when
prodromal proportional to dose received death occurs rapidly
stage
Latent period Hours to days Apparent clinical Days to weeks, inversely related to dose
improvement
Manifest 3 5 weeks Cerebrovascular injury Variable, until death or recovery
illness
Pulmonary disease
Gastrointestinal syndrome
Hematopoietic syndrome
Cutaneous syndrome
Recovery Variable Clinical improvement and Weeks to months
eventual recovery
Source: Adapted from Rella, J.G., 2015. Radiation. In Hoffman, R.S., Howland, M.A., Lewin, N.A., Nelson, L.S., Goldfrank, L.R. (Eds.), Goldfrank’s
Toxicologic Emergencies (10th ed.) (pp. 1703-1712). McGraw-Hill Education, New York.