Page 99 - Clinical Manual of Small Animal Endosurgery
P. 99
Operative Arthroscopy 87
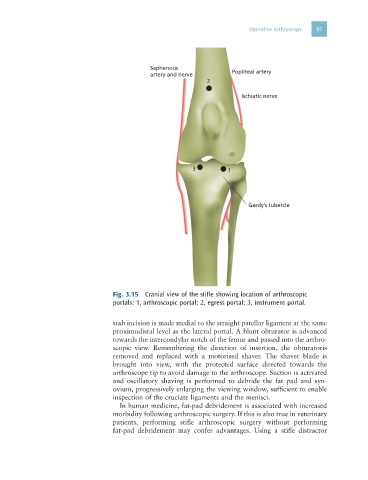
Saphenous
artery and nerve Popliteal artery
2
lschiatic nerve
3 1
Gerdy’s tubercle
Fig. 3.15 Cranial view of the stifle showing location of arthroscopic
portals: 1, arthroscopic portal; 2, egress portal; 3, instrument portal.
stab incision is made medial to the straight patellar ligament at the same
proximodistal level as the lateral portal. A blunt obturator is advanced
towards the intercondylar notch of the femur and passed into the arthro-
scopic view. Remembering the direction of insertion, the obturatoris
removed and replaced with a motorised shaver. The shaver blade is
brought into view, with the protected surface directed towards the
arthroscope tip to avoid damage to the arthroscope. Suction is activated
and oscillatory shaving is performed to debride the fat pad and syn-
ovium, progressively enlarging the viewing window, sufficient to enable
inspection of the cruciate ligaments and the menisci.
In human medicine, fat-pad debridement is associated with increased
morbidity following arthroscopic surgery. If this is also true in veterinary
patients, performing stifle arthroscopic surgery without performing
fat-pad debridement may confer advantages. Using a stifle distractor