Page 63 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 63
Answers 5, 6 ECG Cases
Answer 5
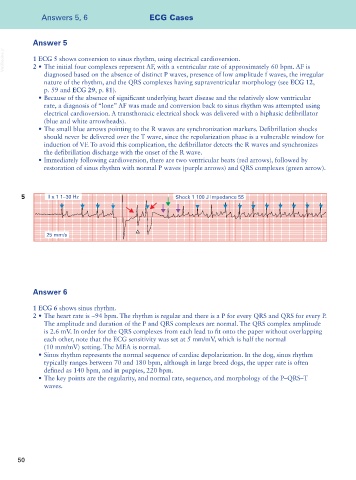
VetBooks.ir 1 ECG 5 shows conversion to sinus rhythm, using electrical cardioversion.
2 • The initial four complexes represent AF, with a ventricular rate of approximately 60 bpm. AF is
diagnosed based on the absence of distinct P waves, presence of low amplitude f waves, the irregular
nature of the rhythm, and the QRS complexes having supraventricular morphology (see ECG 12,
p. 59 and ECG 29, p. 81).
• Because of the absence of significant underlying heart disease and the relatively slow ventricular
rate, a diagnosis of “lone” AF was made and conversion back to sinus rhythm was attempted using
electrical cardioversion. A transthoracic electrical shock was delivered with a biphasic defibrillator
(blue and white arrowheads).
• The small blue arrows pointing to the R waves are synchronization markers. Defibrillation shocks
should never be delivered over the T wave, since the repolarization phase is a vulnerable window for
induction of VF. To avoid this complication, the defibrillator detects the R waves and synchronizes
the defibrillation discharge with the onset of the R wave.
• Immediately following cardioversion, there are two ventricular beats (red arrows), followed by
restoration of sinus rhythm with normal P waves (purple arrows) and QRS complexes (green arrow).
5 II x 1 1–30 Hz Shock 1 100 J Impedance 55
25 mm/s
Answer 6
1 ECG 6 shows sinus rhythm.
2 • The heart rate is ~94 bpm. The rhythm is regular and there is a P for every QRS and QRS for every P.
The amplitude and duration of the P and QRS complexes are normal. The QRS complex amplitude
is 2.6 mV. In order for the QRS complexes from each lead to fit onto the paper without overlapping
each other, note that the ECG sensitivity was set at 5 mm/mV, which is half the normal
(10 mm/mV) setting. The MEA is normal.
• Sinus rhythm represents the normal sequence of cardiac depolarization. In the dog, sinus rhythm
typically ranges between 70 and 180 bpm, although in large breed dogs, the upper rate is often
defined as 140 bpm, and in puppies, 220 bpm.
• The key points are the regularity, and normal rate, sequence, and morphology of the P–QRS–T
waves.
50