Page 67 - Rapid Review of ECG Interpretation in Small Animal Practice, 2nd Edition
P. 67
Answer 9 ECG Cases
Answer 9
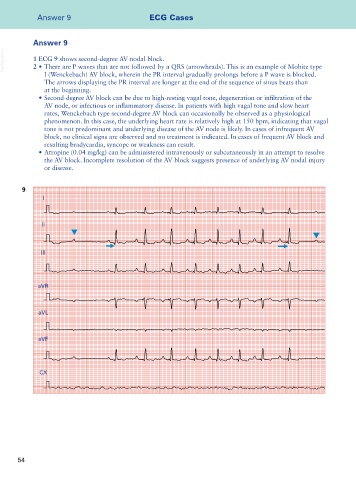
VetBooks.ir 1 ECG 9 shows second-degree AV nodal block.
2 • There are P waves that are not followed by a QRS (arrowheads). This is an example of Mobitz type
I (Wenckebach) AV block, wherein the PR interval gradually prolongs before a P wave is blocked.
The arrows displaying the PR interval are longer at the end of the sequence of sinus beats than
at the beginning.
• Second-degree AV block can be due to high-resting vagal tone, degeneration or infiltration of the
AV node, or infectious or inflammatory disease. In patients with high vagal tone and slow heart
rates, Wenckebach type second-degree AV block can occasionally be observed as a physiological
phenomenon. In this case, the underlying heart rate is relatively high at 150 bpm, indicating that vagal
tone is not predominant and underlying disease of the AV node is likely. In cases of infrequent AV
block, no clinical signs are observed and no treatment is indicated. In cases of frequent AV block and
resulting bradycardia, syncope or weakness can result.
• Atropine (0.04 mg/kg) can be administered intravenously or subcutaneously in an attempt to resolve
the AV block. Incomplete resolution of the AV block suggests presence of underlying AV nodal injury
or disease.
9
I
II
III
aVR
aVL
aVF
CX
54