Page 168 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 168
158 ELECTROLYTE DISORDERS
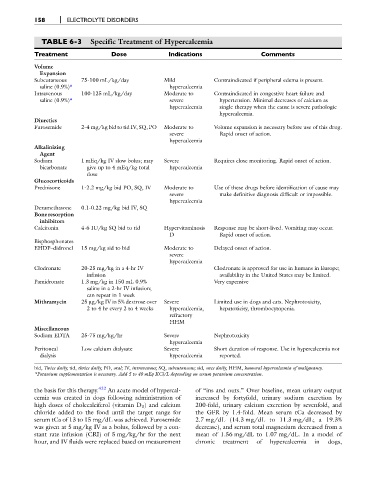
TABLE 6-3 Specific Treatment of Hypercalcemia
Treatment Dose Indications Comments
Volume
Expansion
Subcutaneous 75-100 mL/kg/day Mild Contraindicated if peripheral edema is present.
saline (0.9%)* hypercalcemia
Intravenous 100-125 mL/kg/day Moderate to Contraindicated in congestive heart failure and
saline (0.9%)* severe hypertension. Minimal decreases of calcium as
hypercalcemia single therapy when the cause is severe pathologic
hypercalcemia.
Diuretics
Furosemide 2-4 mg/kg bid to tid IV, SQ, PO Moderate to Volume expansion is necessary before use of this drug.
severe Rapid onset of action.
hypercalcemia
Alkalinizing
Agent
Sodium 1 mEq/kg IV slow bolus; may Severe Requires close monitoring. Rapid onset of action.
bicarbonate give up to 4 mEq/kg total hypercalcemia
dose
Glucocorticoids
Prednisone 1-2.2 mg/kg bid PO, SQ, IV Moderate to Use of these drugs before identification of cause may
severe make definitive diagnosis difficult or impossible.
hypercalcemia
Dexamethasone 0.1-0.22 mg/kg bid IV, SQ
Bone resorption
inhibitors
Calcitonin 4-6 IU/kg SQ bid to tid Hypervitaminosis Response may be short-lived. Vomiting may occur.
D Rapid onset of action.
Bisphosphonates
EHDP–didronel 15 mg/kg sid to bid Moderate to Delayed onset of action.
severe
hypercalcemia
Clodronate 20-25 mg/kg in a 4-hr IV Clodronate is approved for use in humans in Europe;
infusion availability in the United States may be limited.
Pamidronate 1.3 mg/kg in 150 mL 0.9% Very expensive
saline in a 2-hr IV infusion;
can repeat in 1 week
Mithramycin 25 mg/kg IV in 5% dextrose over Severe Limited use in dogs and cats. Nephrotoxicity,
2 to 4 hr every 2 to 4 weeks hypercalcemia, hepatoxicity, thrombocytopenia.
refractory
HHM
Miscellaneous
Sodium EDTA 25-75 mg/kg/hr Severe Nephrotoxicity
hypercalcemia
Peritoneal Low calcium dialysate Severe Short duration of response. Use in hypercalcemia not
dialysis hypercalcemia reported.
bid, Twice daily; tid, thrice daily; PO, oral; IV, intravenous; SQ, subcutaneous; sid, once daily; HHM, humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy.
*Potassium supplementation is necessary. Add 5 to 40 mEq KCl/L depending on serum potassium concentration.
the basis for this therapy. 422 An acute model of hypercal- of “ins and outs.” Over baseline, mean urinary output
cemia was created in dogs following administration of increased by fortyfold, urinary sodium excretion by
high doses of cholecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) and calcium 200-fold, urinary calcium excretion by sevenfold, and
chloride added to the food until the target range for the GFR by 1.4-fold. Mean serum tCa decreased by
serum tCa of 13 to 15 mg/dL was achieved. Furosemide 2.7 mg/dL (14.3 mg/dL to 11.3 mg/dL; a 19.3%
was given at 5 mg/kg IV as a bolus, followed by a con- decrease), and serum total magnesium decreased from a
stant rate infusion (CRI) of 5 mg/kg/hr for the next mean of 1.56 mg/dL to 1.07 mg/dL. In a model of
hour, and IV fluids were replaced based on measurement chronic treatment of hypercalcemia in dogs,