Page 95 - Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Disorders in Small Animal Practice
P. 95
Disorders of Chloride: Hyperchloremia and Hypochloremia 85
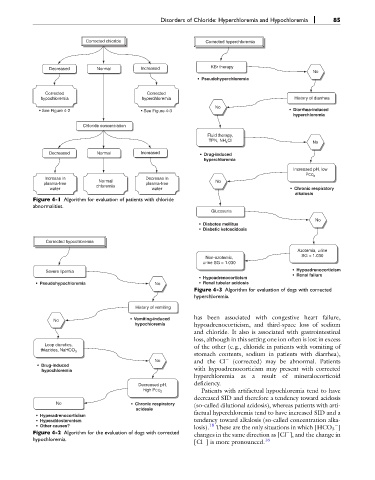
Corrected chloride Corrected hyperchloremia
KBr therapy
Decreased Normal Increased
No
• Pseudohyperchloremia
Corrected Corrected
hypochloremia hyperchloremia History of diarrhea
No
• See Figure 4-2 • See Figure 4-3 • Diarrhea-induced
hyperchloremia
Chloride concentration
Fluid therapy,
TPN, NH Cl
4 No
Decreased Normal Increased • Drug-induced
hyperchloremia
Increased pH, low
PCO 2
Increase in Decrease in
Normal No
plasma-free chloremia plasma-free
water water • Chronic respiratory
alkalosis
Figure 4-1 Algorithm for evaluation of patients with chloride
abnormalities.
Glucosuria
No
• Diabetes mellitus
• Diabetic ketoacidosis
Corrected hypochloremia
Azotemia, urine
SG < 1.030
Non-azotemic,
urine SG > 1.030
Severe lipemia • Hypoadrenocorticism
• Renal failure
• Hypoadrenocorticism
• Pseudohypochloremia No • Renal tubular acidosis
Figure 4-3 Algorithm for evaluation of dogs with corrected
hyperchloremia.
History of vomiting
• Vomiting-induced has been associated with congestive heart failure,
No
hypochloremia hypoadrenocorticism, and third-space loss of sodium
and chloride. It also is associated with gastrointestinal
loss, although in this setting one ion often is lost in excess
Loop diuretics,
thiazides, NaHCO 3 of the other (e.g., chloride in patients with vomiting of
stomach contents, sodium in patients with diarrhea),
No and the Cl (corrected) may be abnormal. Patients
• Drug-induced
hypochloremia with hypoadrenocorticism may present with corrected
hyperchloremia as a result of mineralocorticoid
deficiency.
Decreased pH,
high PCO Patients with artifactual hypochloremia tend to have
2
decreased SID and therefore a tendency toward acidosis
No • Chronic respiratory (so-called dilutional acidosis), whereas patients with arti-
acidesie
factual hyperchloremia tend to have increased SID and a
• Hyperadrenocorticism
• Hyperaldosteronism tendency toward alkalosis (so-called concentration alka-
• Other causes? losis). 18 These are the only situations in which [HCO 3 ]
Figure 4-2 Algorithm for the evaluation of dogs with corrected changes in the same direction as [Cl ], and the change in
hypochloremia. 16
[Cl ] is more pronounced.