Page 138 - Feline Cardiology
P. 138
Chapter 11: Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy 137
with mild agitation (i.e., mildly startling the cat) allows graphic severity of SAM should be placed in its indi-
measurement of the maximal aortic blood flow velocity vidual context for each cat based on the cat’s character,
and greatest severity of SAM. Cats are typically anxious daily routine, medications, and similar variables.
and catecholamine driven in the veterinary hospital
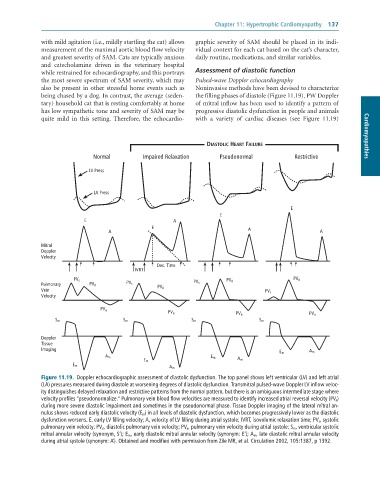
while restrained for echocardiography, and this portrays Assessment of diastolic function
the most severe spectrum of SAM severity, which may Pulsed-wave Doppler echocardiography
also be present in other stressful home events such as Noninvasive methods have been devised to characterize
being chased by a dog. In contrast, the average (seden- the filling phases of diastole (Figure 11.19). PW Doppler
tary) household cat that is resting comfortably at home of mitral inflow has been used to identify a pattern of
has low sympathetic tone and severity of SAM may be progressive diastolic dysfunction in people and animals
o
f
e,
r
he
T
e
r
car
dio
quite mild in this setting. Therefore, the echocardio- - with a variety of cardiac diseases (see Figure 11.19)
ho
the
e
c
DIASTOLIC HEART FAILURE Cardiomyopathies
Normal Impaired Relaxation Pseudonormal Restrictive
LV Press
LA Press
E
E
E A
E A
A A
Mitral
Doppler
Velocity
Dec. Time
IVRT
PV d
PV s PV d
Pulmonary PV d PV s PV s
PV d
Vein
PV s
Velocity
PV a
PV a
PV a PV a
S m S m S m S m
Doppler
Tissue
Imaging
E m A m
A m E m
A m
E m
E m
A m
Figure 11.19. Doppler echocardiographic assessment of diastolic dysfunction. The top panel shows left ventricular (LV) and left atrial
(LA) pressures measured during diastole at worsening degrees of diastolic dysfunction. Transmitral pulsed-wave Doppler LV inflow veloc-
ity distinguishes delayed relaxation and restrictive patterns from the normal pattern, but there is an ambiguous intermediate stage where
velocity profiles “pseudonormalize.” Pulmonary vein blood flow velocities are measured to identify increased atrial reversal velocity (PV a)
during more severe diastolic impairment and sometimes in the pseudonormal phase. Tissue Doppler imaging of the lateral mitral an-
nulus shows reduced early diastolic velocity (E m) in all levels of diastolic dysfunction, which becomes progressively lower as the diastolic
dysfunction worsens. E, early LV filling velocity; A, velocity of LV filling during atrial systole; IVRT, isovolumic relaxation time; PV s, systolic
pulmonary vein velocity; PV d , diastolic pulmonary vein velocity; PV a , pulmonary vein velocity during atrial systole; S m, ventricular systolic
mitral annular velocity (synonym, S’); E m , early diastolic mitral annular velocity (synonym: E’); A m, late diastolic mitral annular velocity
during atrial systole (synonym: A’). Obtained and modified with permission from Zile MR, et al. Circulation 2002, 105:1387, p 1392.