Page 311 - Feline Cardiology
P. 311
Chapter 20: Arterial Thromboembolism 319
RK α the coagulation cascade at multiple sites beyond their
primary effect on factor Xa (platelet function, tissue
factor-endothelial cell interactions and antithrombin
activity), TEG, which provides a global assessment of the
MA clotting process, may be superior to monitoring with
anti-Xa activity levels (Klein et al. 2000).
Combined Anticoagulation Therapy
Human clinical trials evaluating combined anticoagu-
Coagulation Fibrinolysis lant therapy (usually warfarin) with antiplatelet therapy
(usually aspirin) have generally concluded that anti-
Precoagulation
platelet treatment alone affords better outcome than
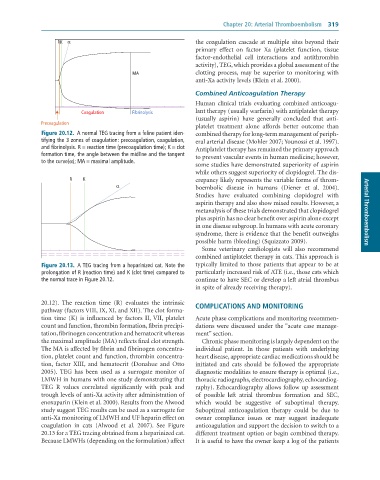
Figure 20.12. A normal TEG tracing from a feline patient iden- combined therapy for long-term management of periph-
tifying the 3 zones of coagulation: precoagulation, coagulation, eral arterial disease (Mohler 2007; Younossi et al. 1997).
and fibrinolysis. R = reaction time (precoagulation time); K = clot Antiplatelet therapy has remained the primary approach
formation time, the angle between the midline and the tangent to prevent vascular events in human medicine; however,
to the curve(α); MA = maximal amplitude.
some studies have demonstrated superiority of aspirin
while others suggest superiority of clopidogrel. The dis-
R K crepancy likely represents the variable forms of throm-
α boembolic disease in humans (Diener et al. 2004).
Studies have evaluated combining clopidogrel with
aspirin therapy and also show mixed results. However, a
metanalysis of these trials demonstrated that clopidogrel Arterial Thromboembolism
plus aspirin has no clear benefit over aspirin alone except
in one disease subgroup. In humans with acute coronary
syndrome, there is evidence that the benefit outweighs
possible harm (bleeding) (Squizzato 2009).
Some veterinary cardiologists will also recommend
combined antiplatelet therapy in cats. This approach is
Figure 20.13. A TEG tracing from a heparinized cat. Note the typically limited to those patients that appear to be at
prolongation of R (reaction time) and K (clot time) compared to particularly increased risk of ATE (i.e., those cats which
the normal trace in Figure 20.12. continue to have SEC or develop a left atrial thrombus
in spite of already receiving therapy).
20.12). The reaction time (R) evaluates the intrinsic COMPLICATIONS AND MONITORING
pathway (factors VIII, IX, XI, and XII). The clot forma-
tion time (K) is influenced by factors II, VII, platelet Acute phase complications and monitoring recommen-
count and function, thrombin formation, fibrin precipi- dations were discussed under the “acute case manage-
tation, fibrinogen concentration and hematocrit whereas ment” section.
the maximal amplitude (MA) reflects final clot strength. Chronic phase monitoring is largely dependent on the
The MA is affected by fibrin and fibrinogen concentra- individual patient. In those patients with underlying
tion, platelet count and function, thrombin concentra- heart disease, appropriate cardiac medications should be
tion, factor XIII, and hematocrit (Donahue and Otto initiated and cats should be followed the appropriate
2005). TEG has been used as a surrogate monitor of diagnostic modalities to ensure therapy is optimal (i.e.,
LMWH in humans with one study demonstrating that thoracic radiographs, electrocardiography, echocardiog-
TEG R values correlated significantly with peak and raphy). Echocardiography allows follow up assessment
trough levels of anti-Xa activity after administration of of possible left atrial thrombus formation and SEC,
enoxaparin (Klein et al. 2000). Results from the Alwood which would be suggestive of suboptimal therapy.
study suggest TEG results can be used as a surrogate for Suboptimal anticoagulation therapy could be due to
anti-Xa monitoring of LMWH and UF heparin effect on owner compliance issues or may suggest inadequate
coagulation in cats (Alwood et al. 2007). See Figure anticoagulation and support the decision to switch to a
20.13 for a TEG tracing obtained from a heparinized cat. different treatment option or begin combined therapy.
Because LMWHs (depending on the formulation) affect It is useful to have the owner keep a log of the patients