Page 326 - Feline Cardiology
P. 326
Chapter 21: Systemic Hypertension 335
4
3
2
1
B
A
C D Systemic Hypertension
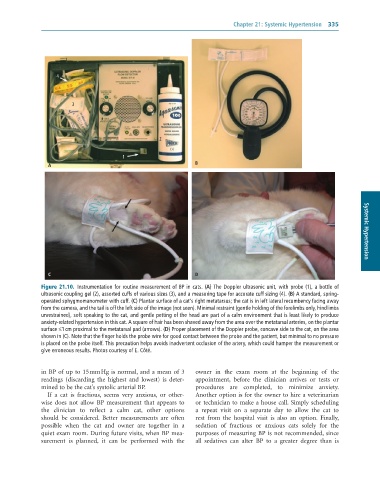
Figure 21.10. Instrumentation for routine measurement of BP in cats. (A) The Doppler ultrasonic unit, with probe (1), a bottle of
ultrasonic coupling gel (2), assorted cuffs of various sizes (3), and a measuring tape for accurate cuff sizing (4). (B) A standard, spring-
operated sphygmomanometer with cuff. (C) Plantar surface of a cat’s right metatarsus; the cat is in left lateral recumbency facing away
from the camera, and the tail is off the left side of the image (not seen). Minimal restraint (gentle holding of the forelimbs only, hindlimbs
unrestrained), soft speaking to the cat, and gentle petting of the head are part of a calm environment that is least likely to produce
anxiety-related hypertension in this cat. A square of hair has been shaved away from the area over the metatarsal arteries, on the plantar
surface ≤1 cm proximal to the metatarsal pad (arrows). (D) Proper placement of the Doppler probe, concave side to the cat, on the area
shown in (C). Note that the finger holds the probe wire for good contact between the probe and the patient, but minimal to no pressure
is placed on the probe itself. This precaution helps avoids inadvertent occlusion of the artery, which could hamper the measurement or
give erroneous results. Photos courtesy of E. Côté.
in BP of up to 15 mm Hg is normal, and a mean of 3 owner in the exam room at the beginning of the
readings (discarding the highest and lowest) is deter appointment, before the clinician arrives or tests or
mined to be the cat’s systolic arterial BP. procedures are completed, to minimize anxiety.
If a cat is fractious, seems very anxious, or other Another option is for the owner to hire a veterinarian
wise does not allow BP measurement that appears to or technician to make a house call. Simply scheduling
the clinician to reflect a calm cat, other options a repeat visit on a separate day to allow the cat to
should be considered. Better measurements are often rest from the hospital visit is also an option. Finally,
possible when the cat and owner are together in a sedation of fractious or anxious cats solely for the
quiet exam room. During future visits, when BP mea purposes of measuring BP is not recommended, since
surement is planned, it can be performed with the all sedatives can alter BP to a greater degree than is