Page 321 - Feline Cardiology
P. 321
330 Section I: Systemic Hypertension
Cardiac
Renal
CNS
Gl?
Genetic?
Environmental Cardiac Sodium
Sympathetic Output Endocrine
Activation Retention Obesity?
Micronutrients?
Stress Hyperthyroidism
Gender? Age?
NO CGRP
–
O COO Na + Substance P
Ang (1–7)
HO Prostaglandin I 2 NH 2 Natriuretic
OH
Systemic Hypertension Bradykinin Adrenomedullin CONH 2 H 2 N HOOC
peptides
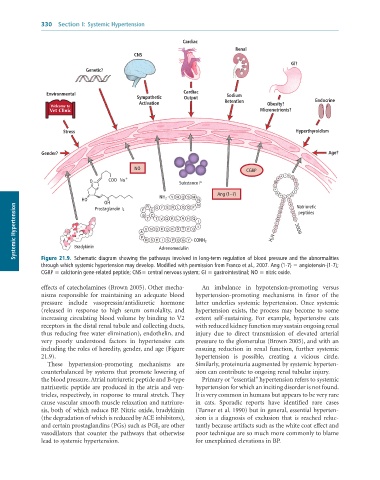
Figure 21.9. Schematic diagram showing the pathways involved in long-term regulation of blood pressure and the abnormalities
through which systemic hypertension may develop. Modified with permission from Franco et al., 2007. Ang (1-7) = angiotensin-(1-7);
CGRP = calcitonin gene-related peptide; CNS= central nervous system; GI = gastrointestinal; NO = nitric oxide.
effects of catecholamines (Brown 2005). Other mecha An imbalance in hypotensionpromoting versus
nisms responsible for maintaining an adequate blood hypertensionpromoting mechanisms in favor of the
pressure include vasopressin/antidiuretic hormone latter underlies systemic hypertension. Once systemic
(released in response to high serum osmolality, and hypertension exists, the process may become to some
increasing circulating blood volume by binding to V2 extent selfsustaining. For example, hypertensive cats
receptors in the distal renal tubule and collecting ducts, with reduced kidney function may sustain ongoing renal
thus reducing free water elimination), endothelin, and injury due to direct transmission of elevated arterial
very poorly understood factors in hypertensive cats pressure to the glomerulus (Brown 2005), and with an
including the roles of heredity, gender, and age (Figure ensuing reduction in renal function, further systemic
21.9). hypertension is possible, creating a vicious circle.
These hypertensionpromoting mechanisms are Similarly, proteinuria augmented by systemic hyperten
counterbalanced by systems that promote lowering of sion can contribute to ongoing renal tubular injury.
the blood pressure. Atrial natriuretic peptide and Btype Primary or “essential” hypertension refers to systemic
natriuretic peptide are produced in the atria and ven hypertension for which an inciting disorder is not found.
tricles, respectively, in response to mural stretch. They It is very common in humans but appears to be very rare
cause vascular smooth muscle relaxation and natriure in cats. Sporadic reports have identified rare cases
sis, both of which reduce BP. Nitric oxide, bradykinin (Turner et al. 1990) but in general, essential hyperten
(the degradation of which is reduced by ACE inhibitors), sion is a diagnosis of exclusion that is reached reluc
and certain prostaglandins (PGs) such as PGI 2 are other tantly because artifacts such as the white coat effect and
vasodilators that counter the pathways that otherwise poor technique are so much more commonly to blame
lead to systemic hypertension. for unexplained elevations in BP.