Page 1180 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 1180
1112 SECTION | XVI Feed and Water Contaminants
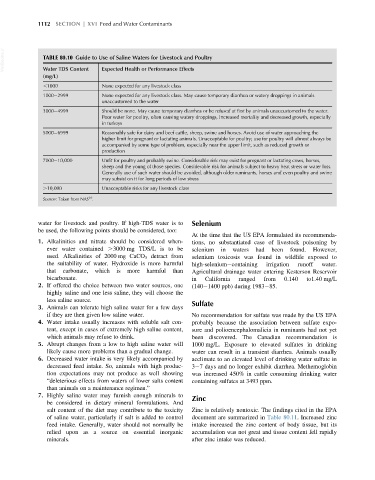
VetBooks.ir TABLE 80.10 Guide to Use of Saline Waters for Livestock and Poultry
Water TDS Content
(mg/L) Expected Health or Performance Effects
,1000 None expected for any livestock class
1000 2999 None expected for any livestock class. May cause temporary diarrhea or watery droppings in animals
unaccustomed to the water
3000 4999 Should be none. May cause temporary diarrhea or be refused at first by animals unaccustomed to the water.
Poor water for poultry, often causing watery droppings, increased mortality and decreased growth, especially
in turkeys
5000 6999 Reasonably safe for dairy and beef cattle, sheep, swine and horses. Avoid use of water approaching the
higher limit for pregnant or lactating animals. Unacceptable for poultry; use for poultry will almost always be
accompanied by some type of problem, especially near the upper limit, such as reduced growth or
production
7000 10,000 Unfit for poultry and probably swine. Considerable risk may exist for pregnant or lactating cows, horses,
sheep and the young of those species. Considerable risk for animals subject to heavy heat stress or water loss.
Generally use of such water should be avoided, although older ruminants, horses and even poultry and swine
may subsist on it for long periods of low stress
.10,000 Unacceptable risks for any livestock class
10
Source: Taken from NAS .
water for livestock and poultry. If high-TDS water is to Selenium
be used, the following points should be considered, too:
At the time that the US EPA formulated its recommenda-
1. Alkalinities and nitrate should be considered when- tions, no substantiated case of livestock poisoning by
ever water contained .3000 mg TDS/L is to be selenium in waters had been found. However,
used. Alkalinities of 2000 mg CaCO 3 detract from selenium toxicosis was found in wildlife exposed to
the suitability of water. Hydroxide is more harmful high-selenium containing irrigation runoff water.
that carbonate, which is more harmful than Agricultural drainage water entering Kesterson Reservoir
bicarbonate. in California ranged from 0.140 to1.40 mg/L
2. If offered the choice between two water sources, one (140 1400 ppb) during 1983 85.
highly saline and one less saline, they will choose the
less saline source. Sulfate
3. Animals can tolerate high saline water for a few days
if they are then given low saline water. No recommendation for sulfate was made by the US EPA
4. Water intake usually increases with soluble salt con- probably because the association between sulfate expo-
tent, except in cases of extremely high saline content, sure and polioencephalomalicia in ruminants had not yet
which animals may refuse to drink. been discovered. The Canadian recommendation is
5. Abrupt changes from a low to high saline water will 1000 mg/L. Exposure to elevated sulfates in drinking
likely cause more problems than a gradual change. water can result in a transient diarrhea. Animals usually
6. Decreased water intake is very likely accompanied by acclimate to an elevated level of drinking water sulfate in
decreased feed intake. So, animals with high produc- 3 7 days and no longer exhibit diarrhea. Methemoglobin
tion expectations may not produce as well showing was increased 450% in cattle consuming drinking water
“deleterious effects from waters of lower salts content containing sulfates at 3493 ppm.
than animals on a maintenance regimen.”
7. Highly saline water may furnish enough minerals to Zinc
be considered in dietary mineral formulations. And
salt content of the diet may contribute to the toxicity Zinc is relatively nontoxic. The findings cited in the EPA
of saline water, particularly if salt is added to control document are summarized in Table 80.11. Increased zinc
feed intake. Generally, water should not normally be intake increased the zinc content of body tissue, but its
relied upon as a source on essential inorganic accumulation was not great and tissue content fell rapidly
minerals. after zinc intake was reduced.