Page 303 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 303
270 SECTION | II Organ Toxicity
VetBooks.ir
(A) (B)
FIGURE 16.2 Ethylene glycol poisoning, canine kidney.
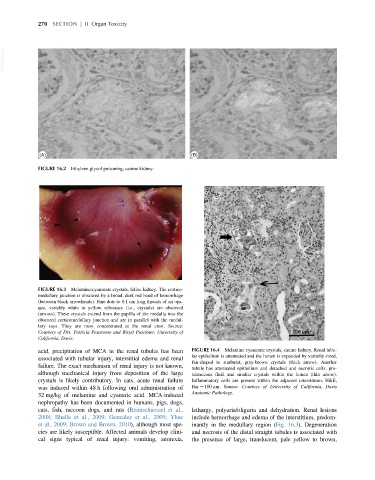
FIGURE 16.3 Melamine:cyanurate crystals, feline kidney. The cortico-
medullary junction is obscured by a broad, dark red band of hemorrhage
(between black arrowheads). Fine dots to 0.1 cm long threads of an opa-
que, variably white to yellow substance (i.e., crystals) are observed
(arrows). These crystals extend from the papilla of the medulla into the
obscured corticomedullary junction and are in parallel with the medul-
lary rays. They are most concentrated at the renal crest. Source:
Courtesy of Drs. Patricia Pesavento and Birgit Puschner, University of
California, Davis.
acid, precipitation of MCA in the renal tubules has been FIGURE 16.4 Melamine:cyanurate crystals, canine kidney. Renal tubu-
lar epithelium is attenuated and the lumen is expanded by variably sized,
associated with tubular injury, interstitial edema and renal
fan-shaped to starburst, gray-brown crystals (thick arrow). Another
failure. The exact mechanism of renal injury is not known,
tubule has attenuated epithelium and detached and necrotic cells, pro-
although mechanical injury from deposition of the large teinaceous fluid and smaller crystals within the lumen (thin arrow).
crystals is likely contributory. In cats, acute renal failure Inflammatory cells are present within the adjacent interstitium. H&E,
was induced within 48 h following oral administration of Bar 5 100 μm. Source: Courtesy of University of California, Davis
Anatomic Pathology.
32 mg/kg of melamine and cyanuric acid. MCA-induced
nephropathy has been documented in humans, pigs, dogs,
cats, fish, raccoon dogs, and rats (Reimschuessel et al., lethargy, polyuria/oliguria and dehydration. Renal lesions
2008; Bhalla et al., 2009; Gonzalez et al., 2009; Yhee include hemorrhage and edema of the interstitium, predom-
et al., 2009; Brown and Brown, 2010), although most spe- inantlyinthe medullary region(Fig. 16.3). Degeneration
cies are likely susceptible. Affected animals develop clini- and necrosis of the distal straight tubules is associated with
cal signs typical of renal injury: vomiting, anorexia, the presence of large, translucent, pale yellow to brown,