Page 864 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 864
836 PART VI Endocrine Disorders
the response of the cat to insulin. Most clients of diabetic cats Home Blood Glucose Monitoring and
are happy with the response to insulin treatment if blood Diabetic Remission
VetBooks.ir glucose concentrations range between 80 and 280 mg/dL A more intensive approach to treating diabetic cats involves
frequent home blood glucose monitoring by the client
throughout the day, and the average blood glucose concen-
tration is less than 250 mg/dL.
The frequency of glucose monitoring is at the discretion and adjusting the insulin dose based on glucose results,
an approach that has the potential to be more aggressive
of the client. If home blood glucose monitoring is not an in maintaining control of blood glucose concentrations,
option, a more conservative, hands-off approach to monitor- increasing the chance for diabetic remission, and potentially
ing and adjusting insulin is taken. In this scenario, micro- delaying the onset of diabetic neuropathy. The key to diabetic
managing the diabetic cat is not recommended, and blood remission lies in the ability to correct insulin resistance and
glucose curves are usually done when the clinician perceives attain and maintain good glycemic control of the diabetic
a need to change insulin therapy. Determination of good state. Home blood glucose monitoring relies on obtaining
versus poor control of glycemia should be based on the cli- capillary blood samples by pricking the inner aspect of the
ent’s subjective opinion of the presence and severity of clini- pinna or the metacarpal or metatarsal pads using a lancet or
cal signs and the overall health of the pet, the ability of the needle and a PBGM device that allows the client to touch the
cat to jump, grooming behavior, findings on physical exami- drop of blood to with the end of the glucose test strip (Fig.
nation, and stability of body weight. Generation of a blood 49.15). The ear and pad prick technique decreases the need
glucose curve is reserved for when problems with control are for physical restraint during sample collection, thereby mini-
perceived. mizing the cat’s discomfort and stress. Accuracy of blood
A B
C
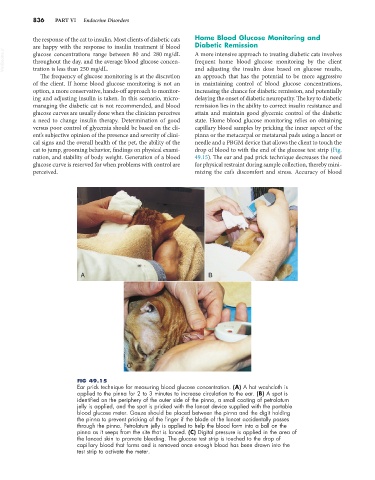
FIG 49.15
Ear prick technique for measuring blood glucose concentration. (A) A hot washcloth is
applied to the pinna for 2 to 3 minutes to increase circulation to the ear. (B) A spot is
identified on the periphery of the outer side of the pinna, a small coating of petrolatum
jelly is applied, and the spot is pricked with the lancet device supplied with the portable
blood glucose meter. Gauze should be placed between the pinna and the digit holding
the pinna to prevent pricking of the finger if the blade of the lancet accidentally passes
through the pinna. Petrolatum jelly is applied to help the blood form into a ball on the
pinna as it seeps from the site that is lanced. (C) Digital pressure is applied in the area of
the lanced skin to promote bleeding. The glucose test strip is touched to the drop of
capillary blood that forms and is removed once enough blood has been drawn into the
test strip to activate the meter.